Part 2
Monthly Ransomware activity
Written by: Maor Huli
Part two will introduce more ransomware activities detected in September
This report will discuss the following:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
What is Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a subscription-based model that lets ransomware developers sell their malicious software to people without any experience in program development.
This model allows the people that bought the software to get constant updates and maintenance from the software developers and thus continue work on new ransomware variants and help with the spread of the existing ones.
The goals for the ransomware authors are either to share the profit from a successful attack or to gain a reputation. The creators consider this a win-win.
What are Ransomware extortions?
We have already observed an evolution in the modus operandi of ransomware. Targeted ransomware attacks by threat groups (also known as “big-game hunting), which include human operated schemes behind them, rely multiple types of extortion:
- Single extortion includes file encryption and demands payment to decrypt the files.
- Double extortion involves threat actors adding a new threat to victims, not only encrypting their files but also threatening to publish sensitive data should the victims refuse to meet threat actors’ demands.
- Triple extortion adds an extra layer by also deploying a distributed-denial-of-service (DDoS) attack on the victim’s encrypted endpoints with the goal of slowing down or preventing the organization’s daily workflow.
- Quadruple extortion adds pressure to pay on top of the previous types mentioned by connecting an organization’s stakeholders to the attack.
CYNET 360 VS RANSOMWARE
Black Matter Ransomware
- Observed since: July 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: Salsa20 + RSA-1024.
- Ransomware extension: .K4Hlh4flg
- Ransomware note: K4Hlh4flg.README.txt
- Sample hash: 520bd9ed608c668810971dbd51184c6a29819674280b018dc4027bc38fc42e57
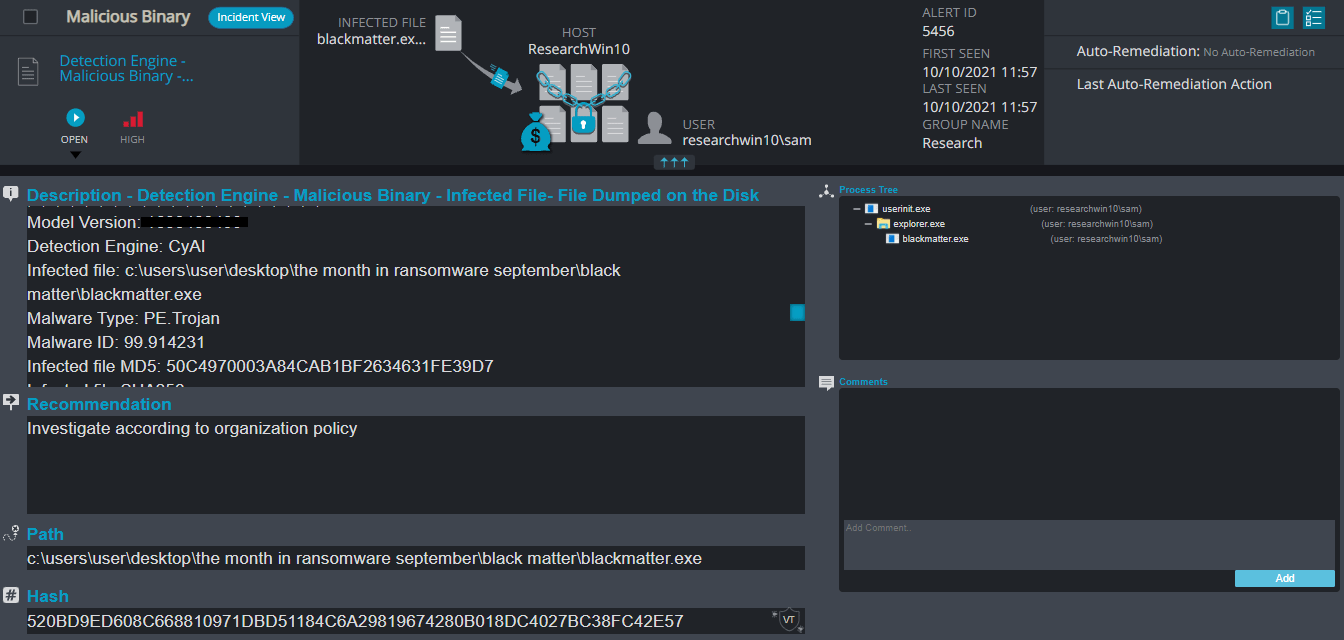
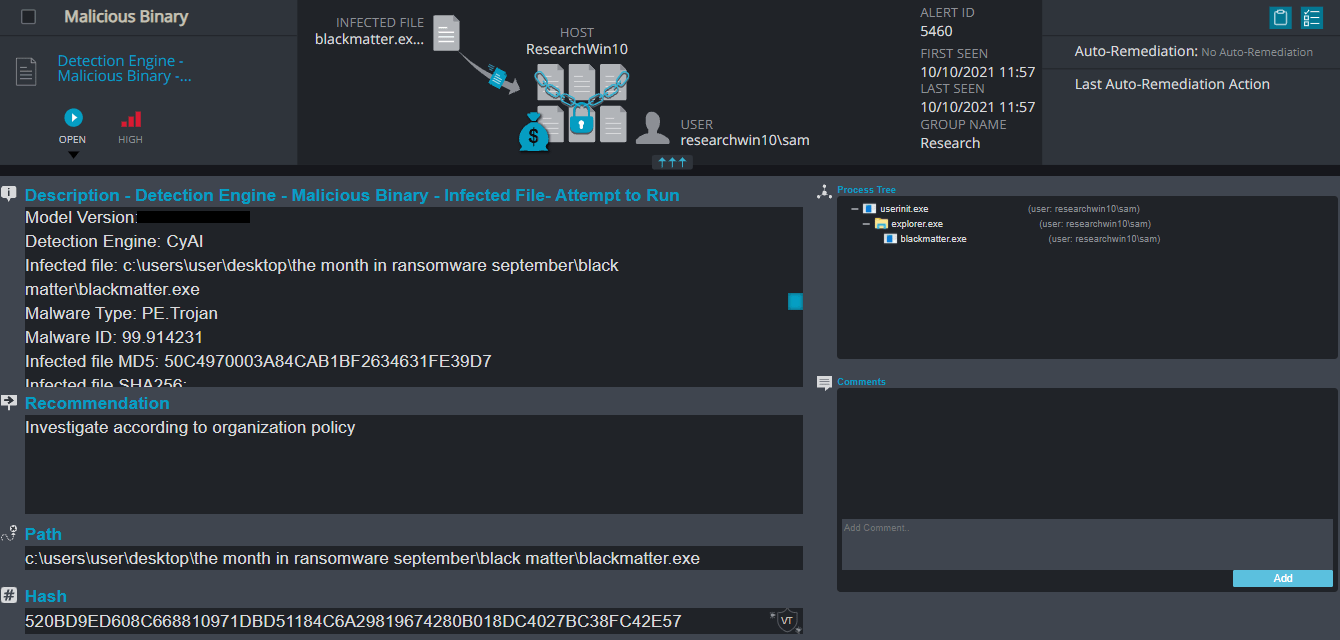
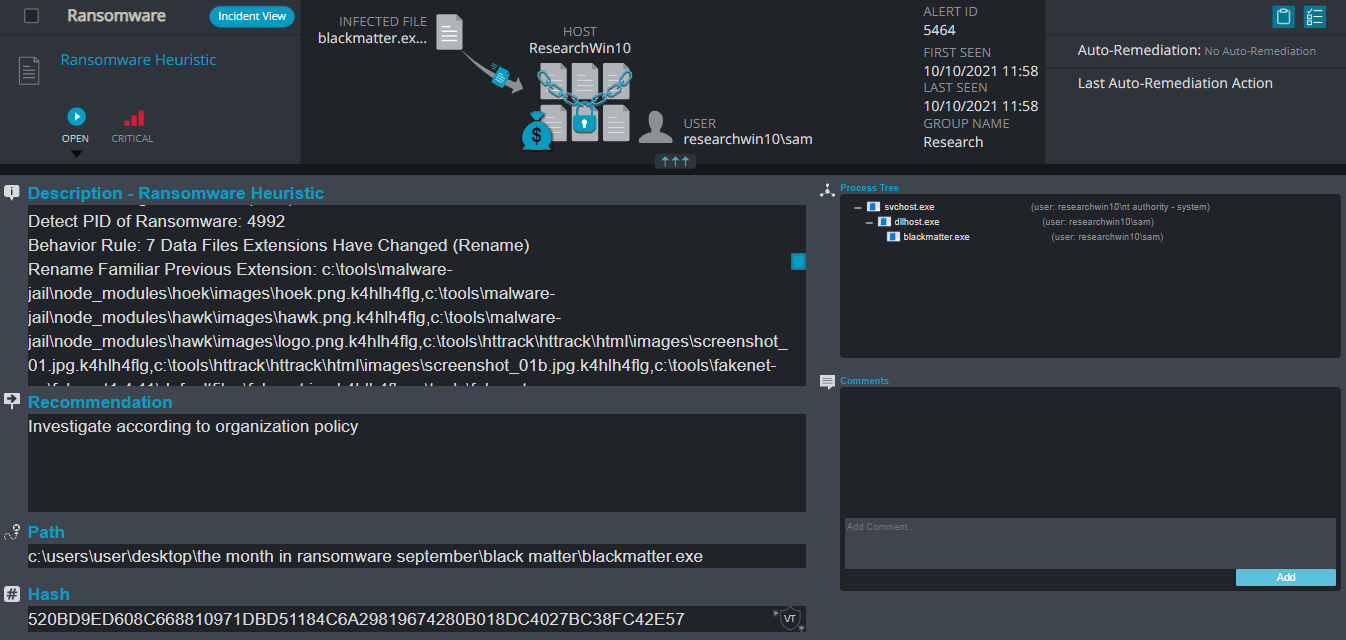
Cynet 360 Detections:
Black Matter Overview
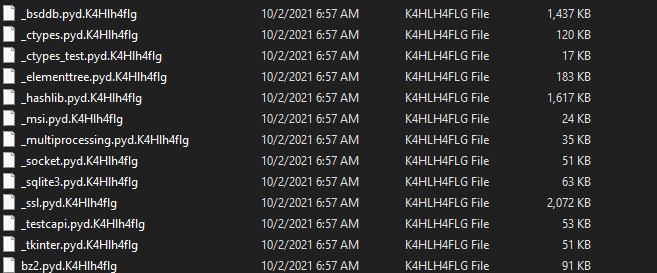
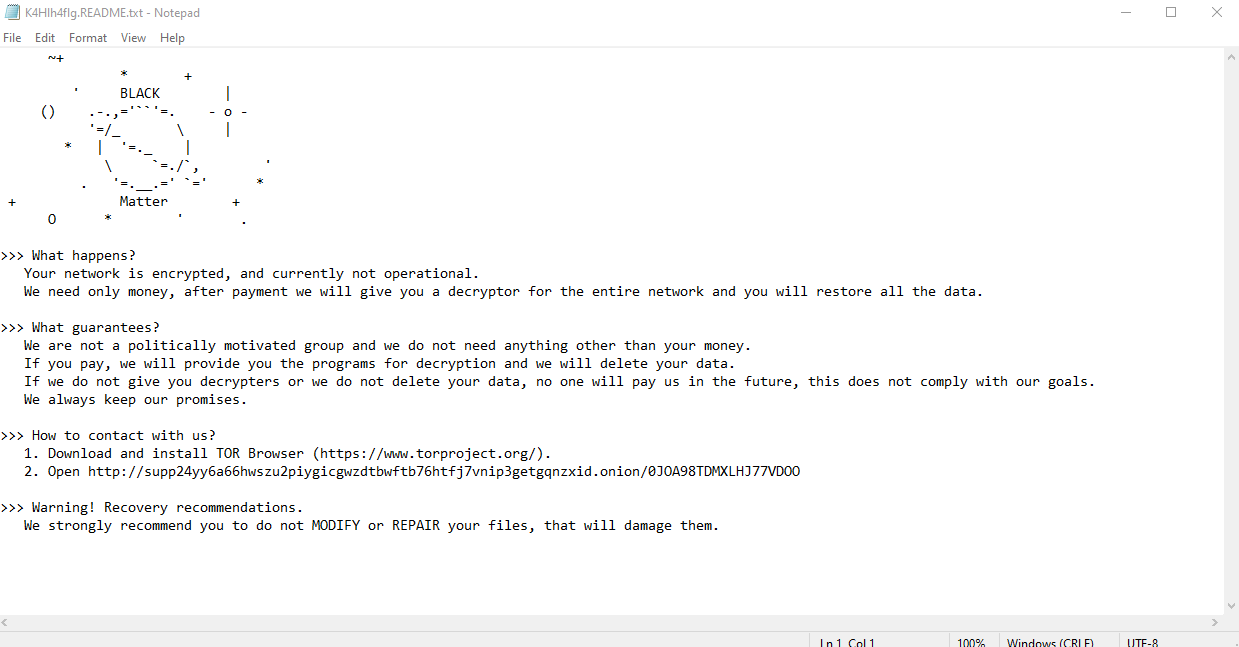
After execution, Black Matter ransomware renames the encrypted files with .K4Hlh4flg in the extension for each file:
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file with the same name of the extension – K4Hlh4flg.README.txt – in the victim’s encrypted folders. The note contains decryption instructions along with the communication details.Additionally, the ransomware changes the desktop background:
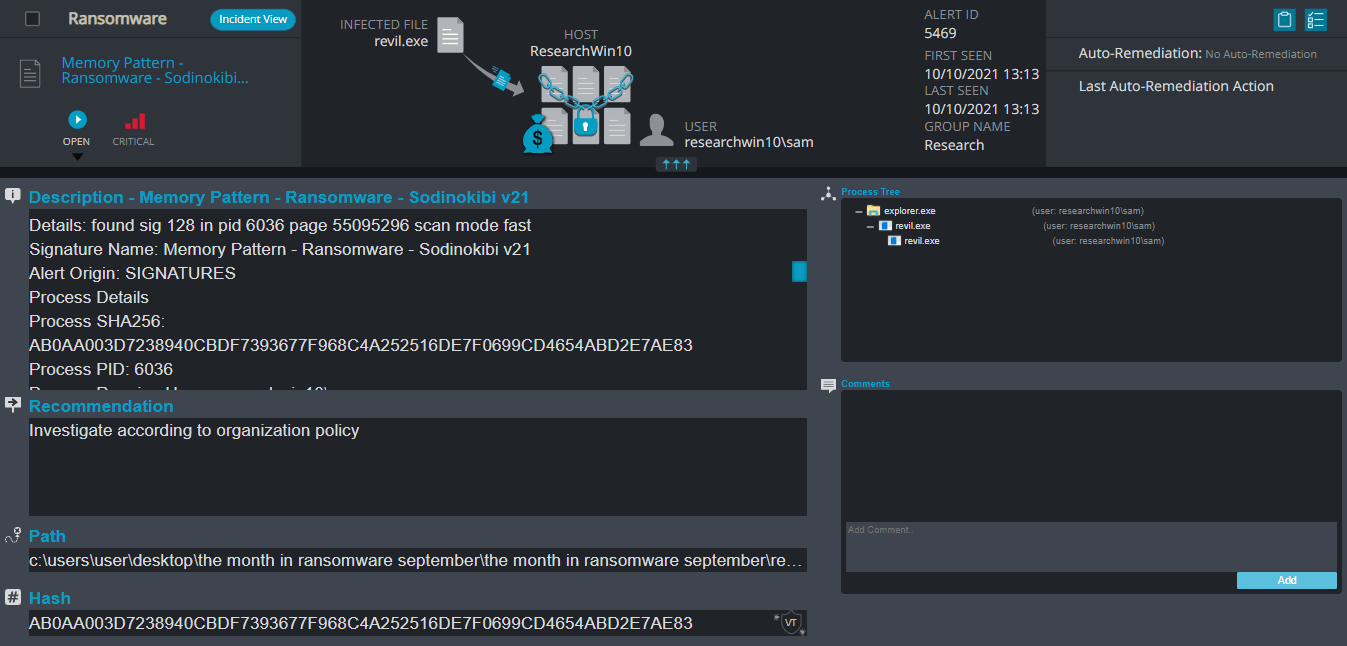
Sodinokibi (REvil) Ransomware
- Observed since: Mid 2019
- Ransomware encryption method: Salsa20.
- Ransomware extension: .random 5-10 strings contains numbers and letters
- Ransomware note: [Random string]-readme.txt
- Sample hash: ab0aa003d7238940cbdf7393677f968c4a252516de7f0699cd4654abd2e7ae83
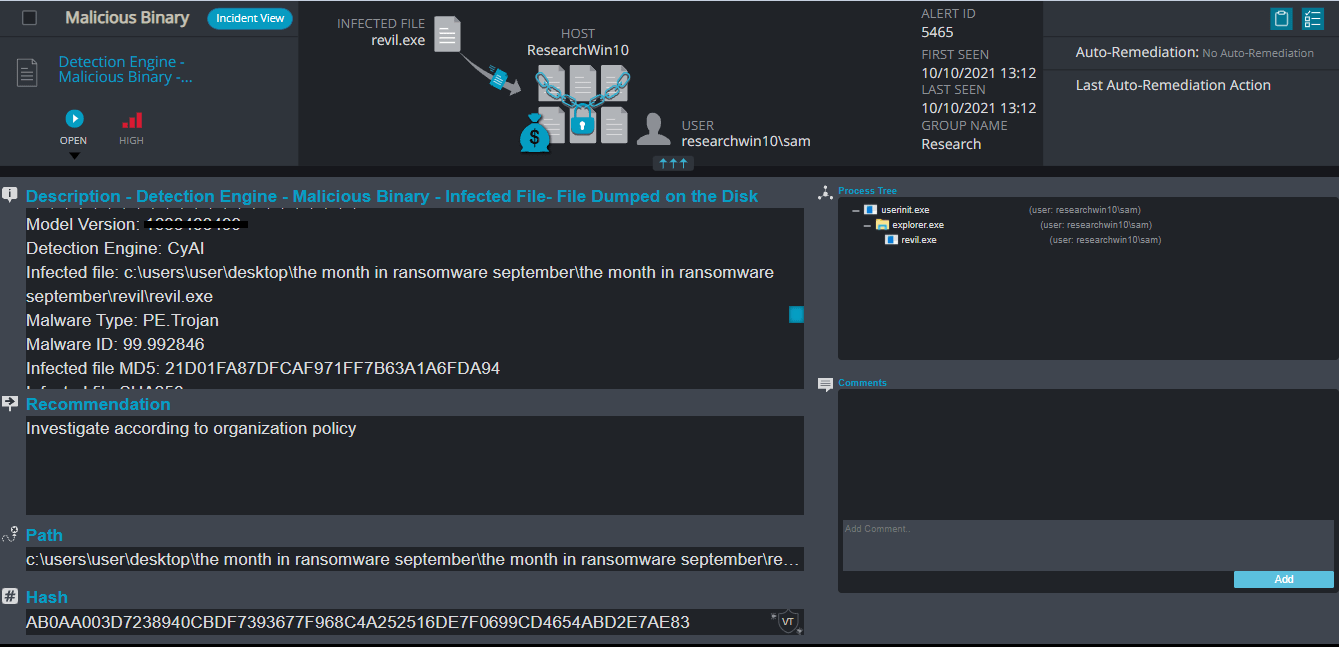
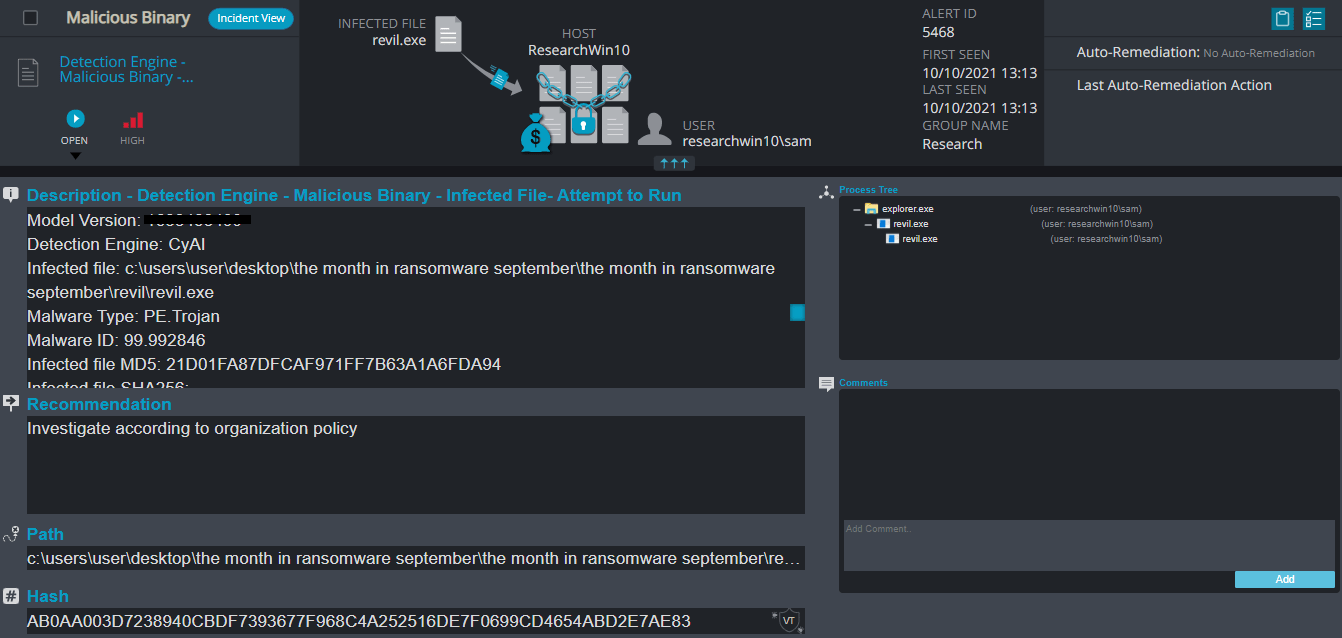
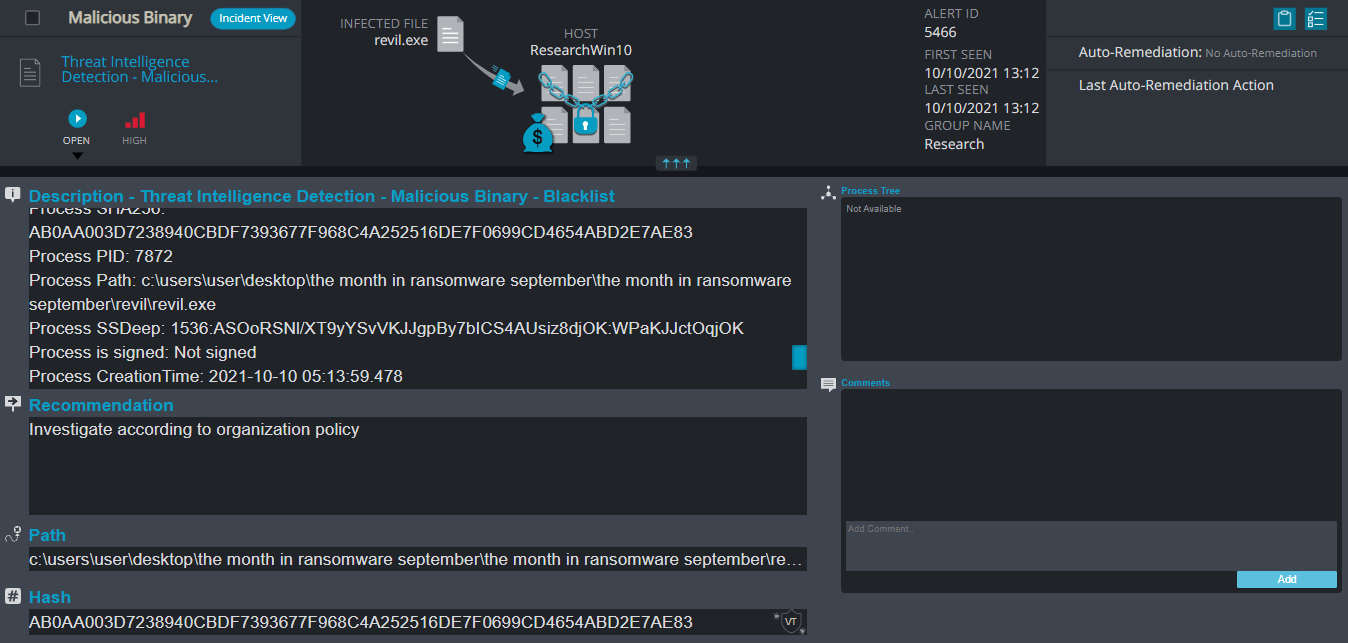
Cynet 360 Detections:
Sodinokibi (REvil) Overview
Please note that since we are running simulations in a virtual environment, some ransomware can distinguish between the real environment and a virtual one. In our case, the ransomware shuts itself down since it detected the virtual environment. The following screenshots are from different sources.
After execution, REvil ransomware renames the encrypted files with random 5-10 letters and numbers in the extension for each file.
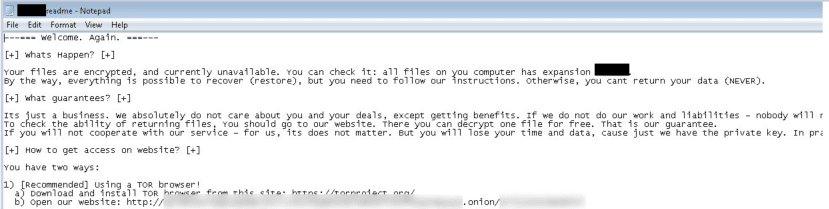
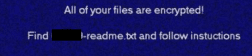
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file with the same name of the random extension [5-10 random numbers and letters]-README.txt in the victim’s encrypted folders. The note contains decryption instructions along with the communication details. Additionally, the ransomware changes the desktop background as well.
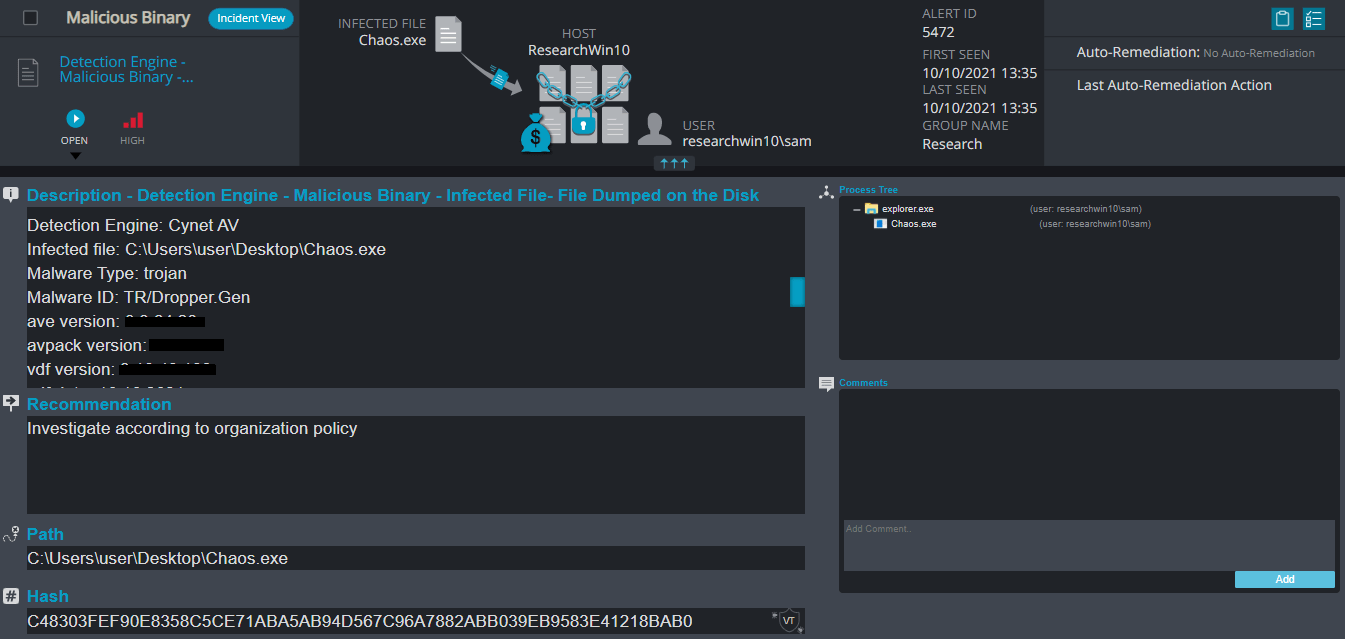
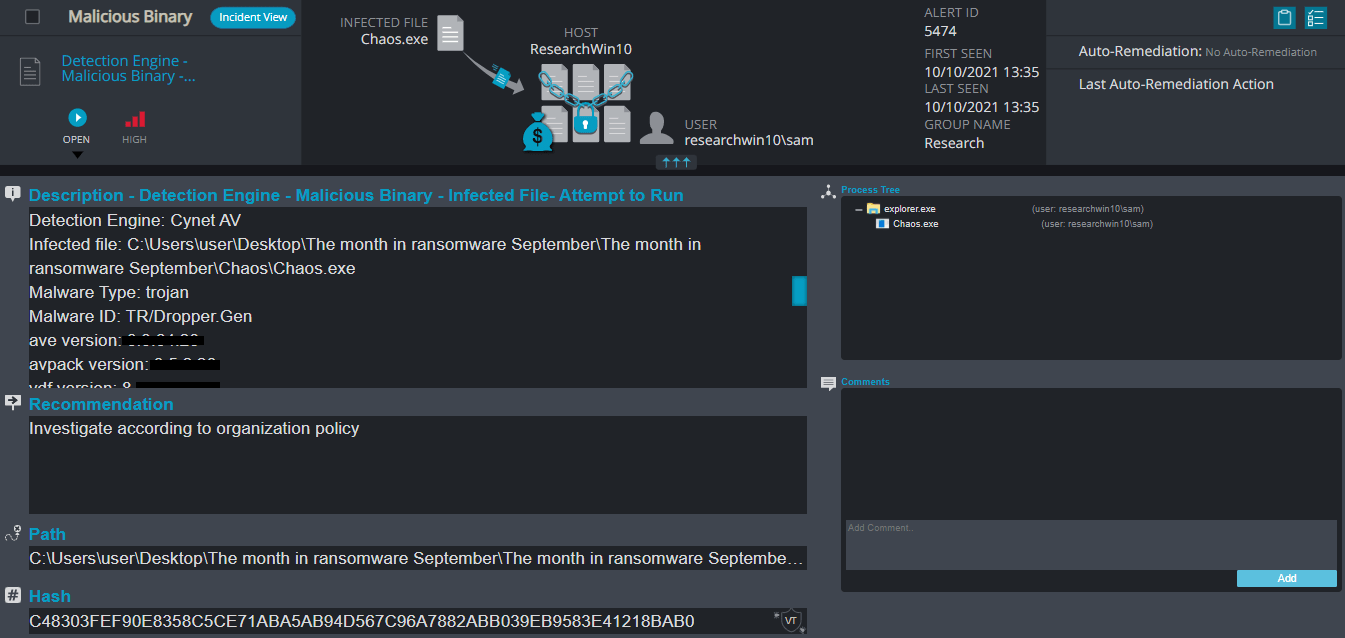
Chaos Ransomware
- Observed since: June 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .CRYPTEDPAY
- Ransomware note: README.txt
- Sample hash: c48303fef90e8358c5ce71aba5ab94d567c96a7882abb039eb9583e41218bab0
Cynet 360 Detections:
Chaos Overview
After execution, Chaos ransomware renames the encrypted files to CRYPTEDPAY in the extension for each file:
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file README.txt in the victim’s encrypted folders. The note contains decryption instructions along with the communication details and the final price for decryption (the attacker asks for the payment with the cryptocurrency Monero). Additionally, the ransomware changes the desktop background as well.
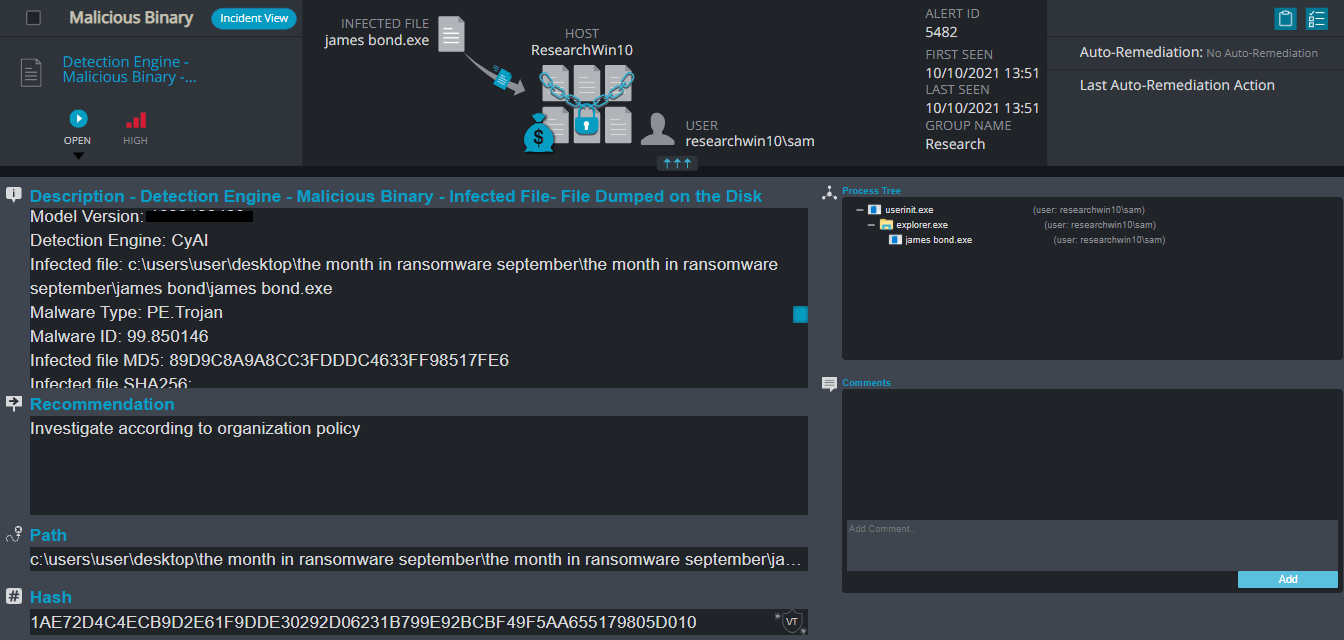
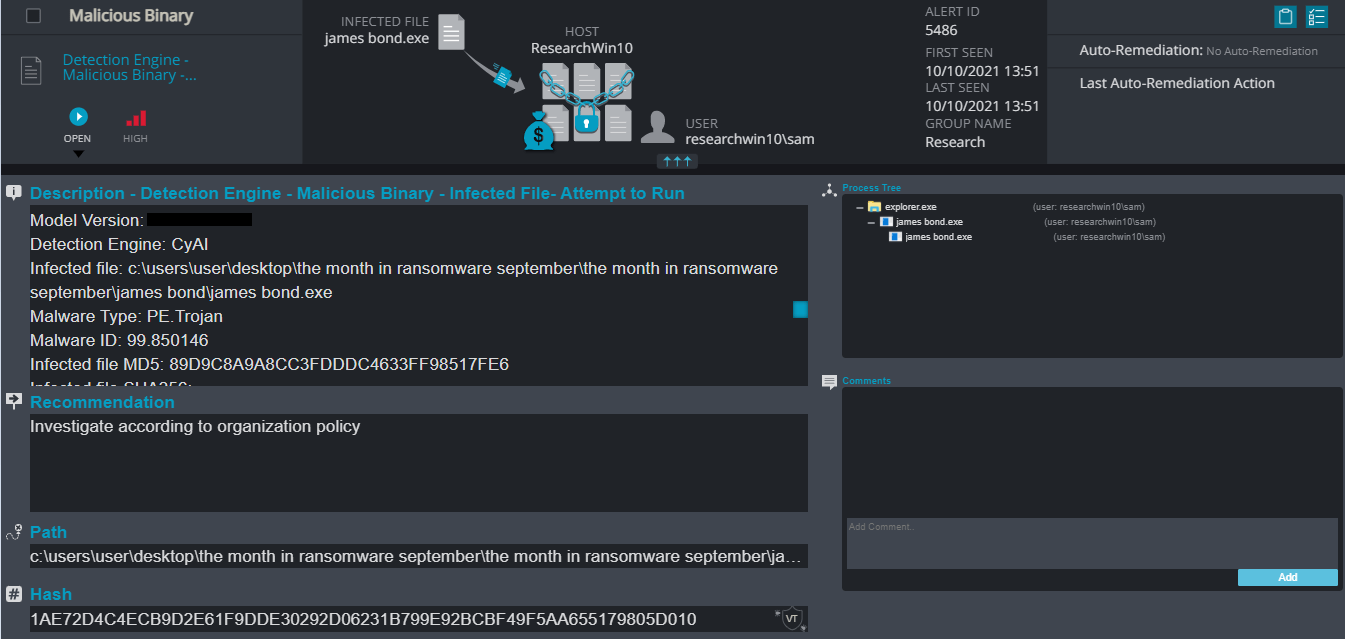
James Bond Ransomware
- Observed since: Late 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
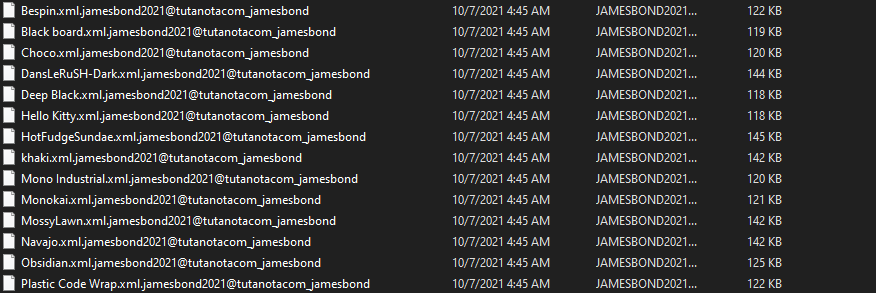
- Ransomware extension: .jamesbond2021@tutanotacom_jamesbond
- Ransomware note: read_it.txt
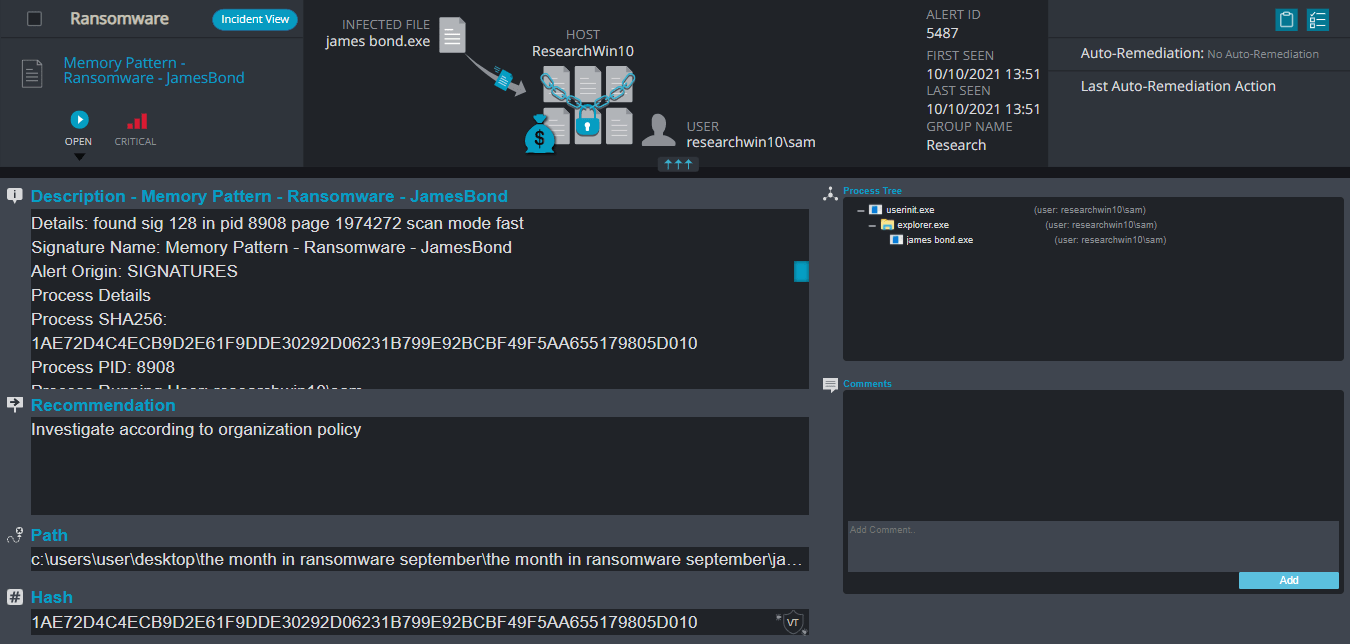
- Sample hash: 1ae72d4c4ecb9d2e61f9dde30292d06231b799e92bcbf49f5aa655179805d010
Cynet 360 Detections:
James Bond Overview
JamesBond ransomware renames the encrypted files to the attacker’s email and the name of the ransomware .jamesbond in the extension for each file:
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file read_it.txt in the victim’s encrypted folders and the desktop. The note contains the communication details. Additionally, the ransomware changes the desktop background as well.
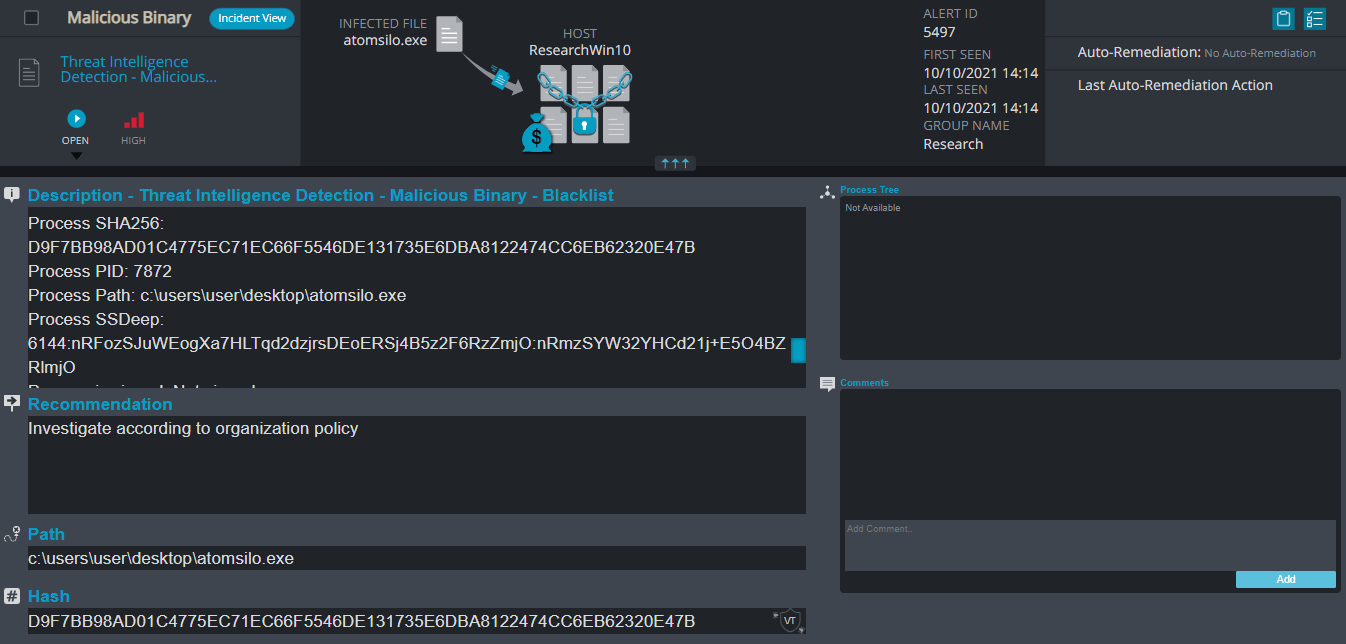
Atom Silo Ransomware
- Observed since: September 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .ATOMSILO
- Ransomware note: README-FILE-[hostname]-[time].hta
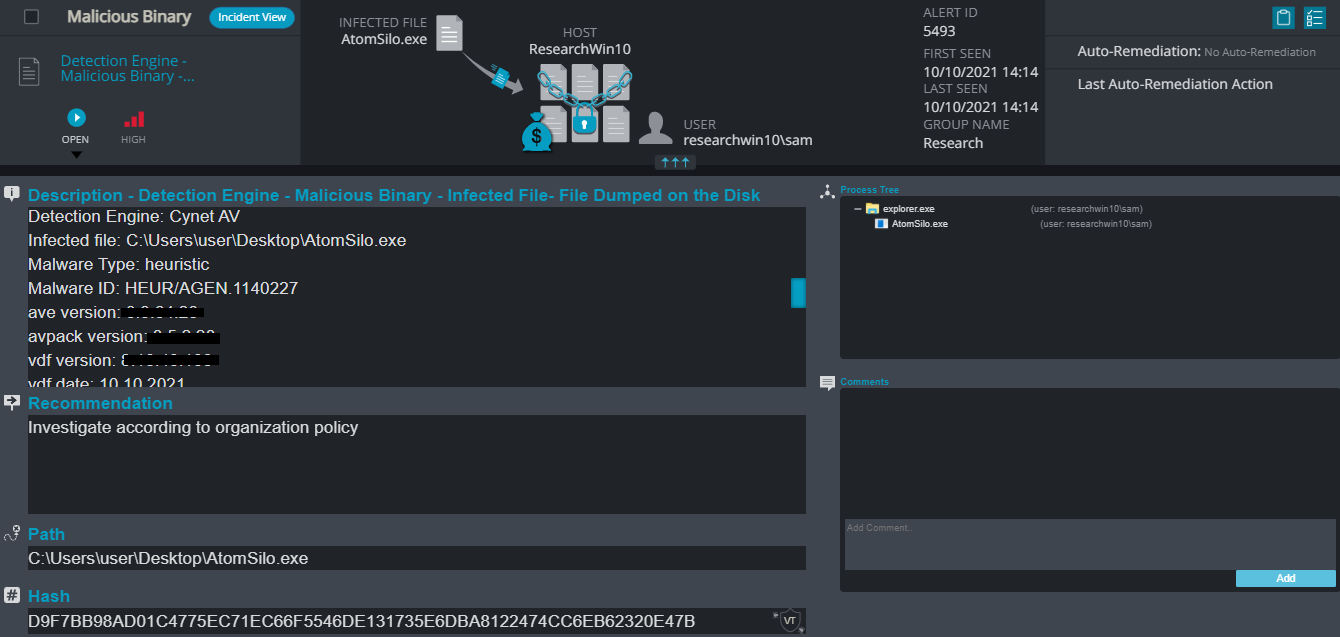
- Sample hash: d9f7bb98ad01c4775ec71ec66f5546de131735e6dba8122474cc6eb62320e47b
Cynet 360 Detections:
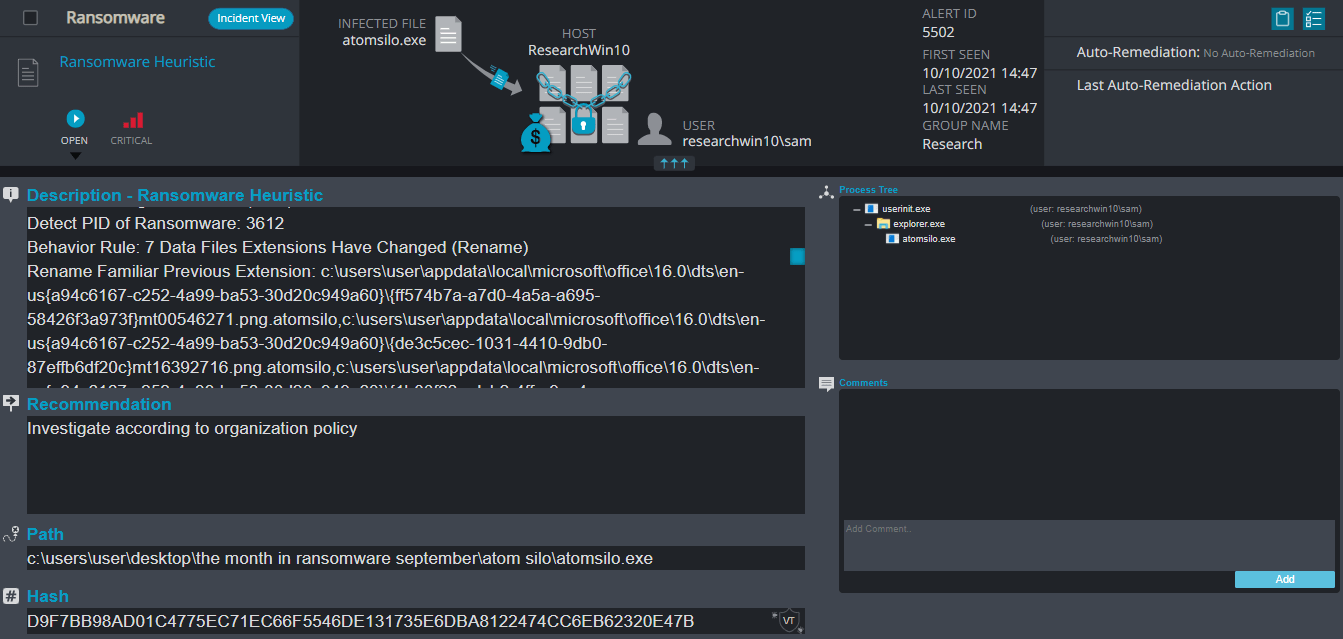
Atom Silo Overview
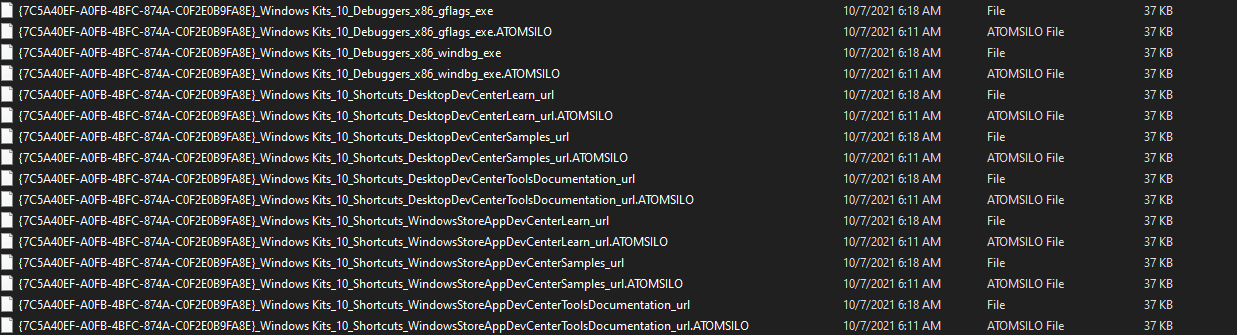
AtomSilo ransomware renames the encrypted files to .ATOMSILO in the extension for each file:
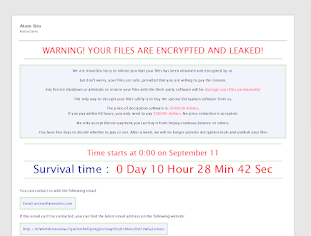
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as an html file that contains the hostname and the time in the name “README-FILE-[hostname]-[time].hta in the victim’s encrypted folders and the desktop. The note contains the communication details along with a demand for $1 million and with a timer that indicates the ransomware will eventually delete the files permanently and will publish the user’s sensitive information as well.
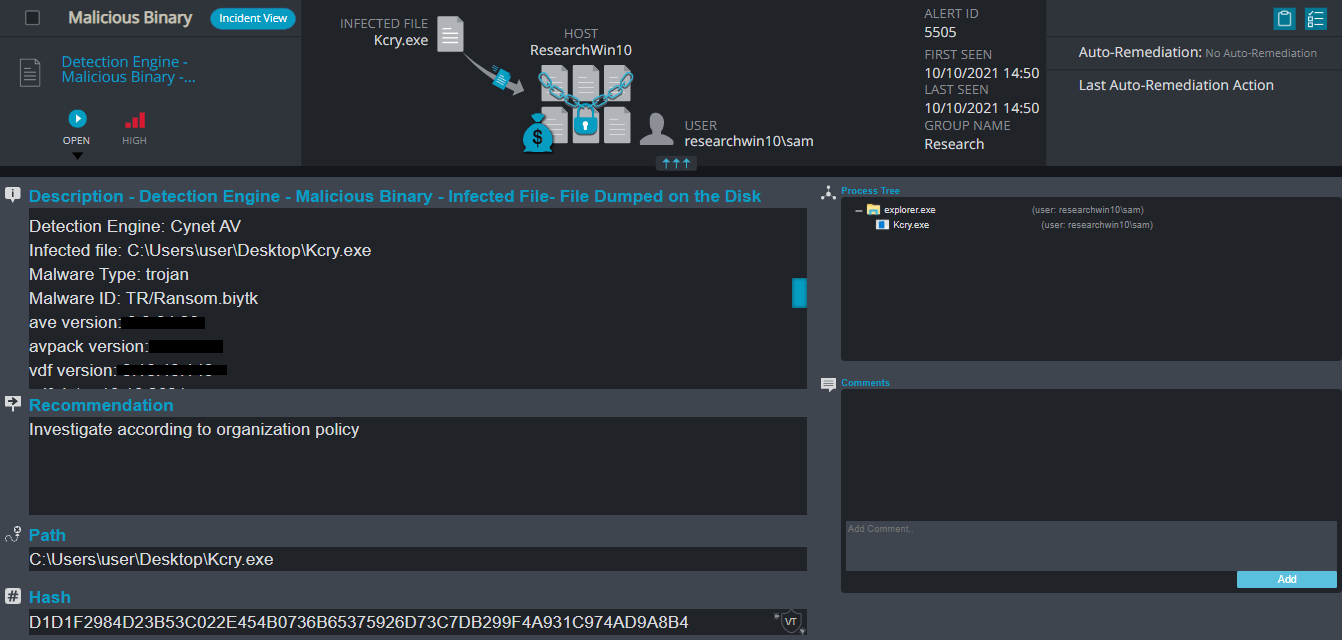
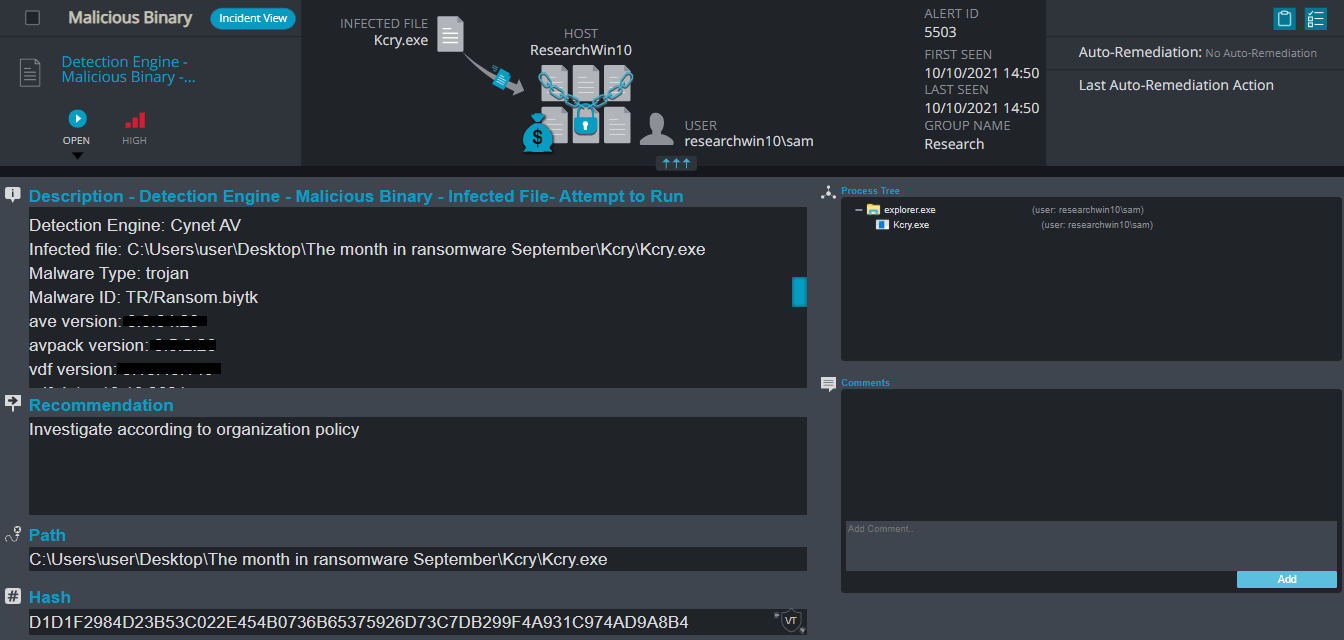
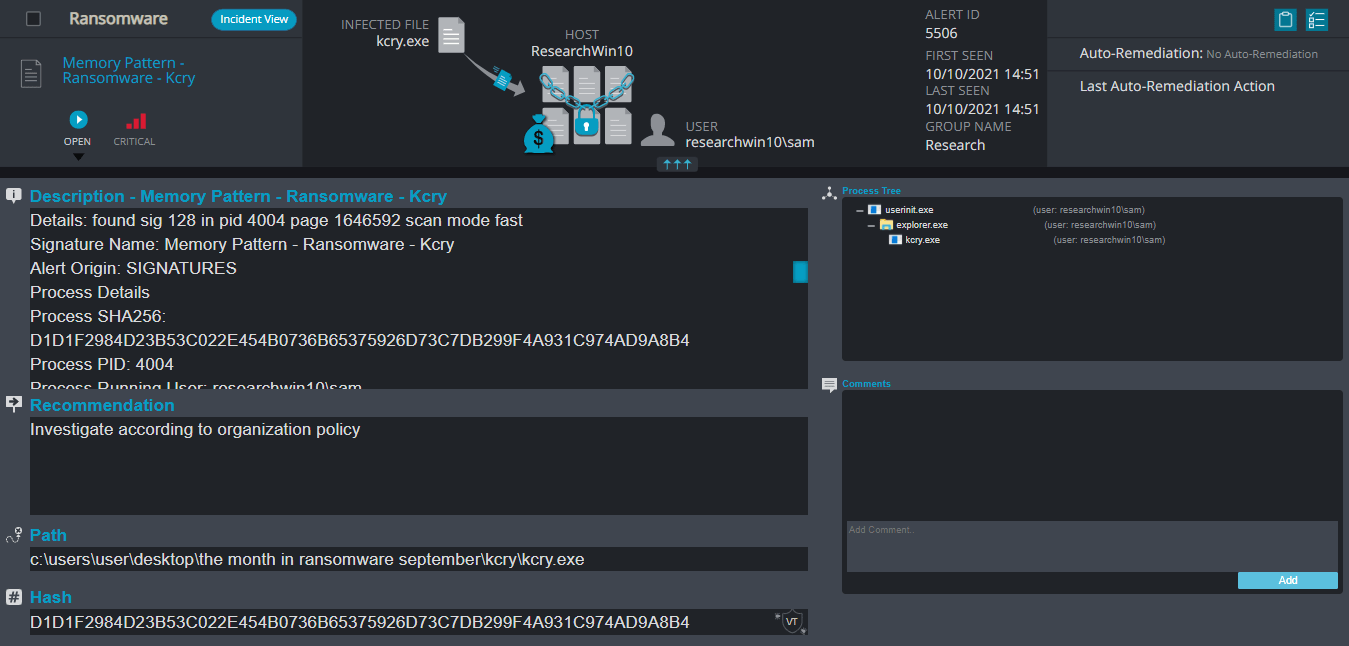
Kcry Ransomware
- Observed since: September 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .kcry
- Ransomware note: kcry-info.txt
- Sample hash: d1d1f2984d23b53c022e454b0736b65375926d73c7db299f4a931c974ad9a8b4
Cynet 360 Detections:
Kcry Overview
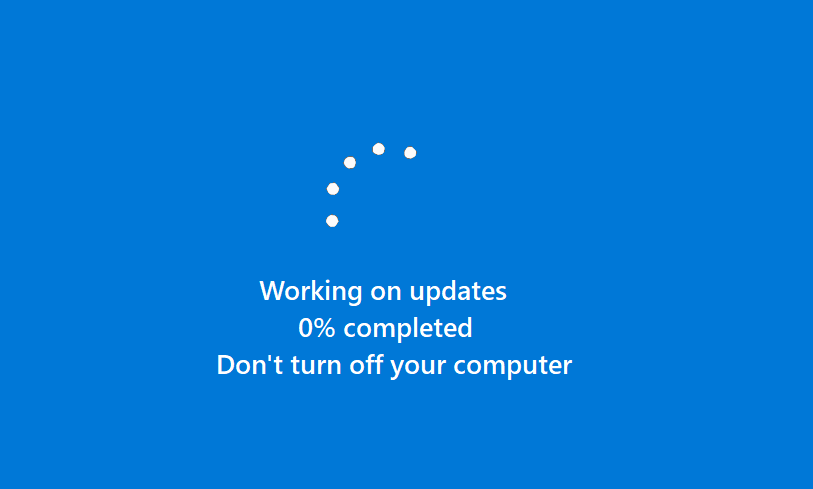
Kcry ransomware changes the host screen for a few seconds to a fake windows update screen, in the meantime, it renames the encrypted files to .kcry in the extension for each file:
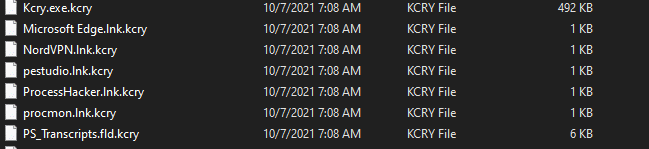
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file that contains the name of the ransomware “kcry-info.txt” in the startup directory for along with a copy of the ransomware executable (for persistence). The note contains the attacker’s itcoin address and a demand for $200 with no guarantee of restoring the files.
Redeemer Ransomware
- Observed since: September 2021
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA.
- Ransomware extension: .redeem
- Ransomware note: Read Me.TXT
- Sample hash: c74873d7b8cc622379ed49bd0b0e477167ae176aa329b01338666ec4c1a4426b
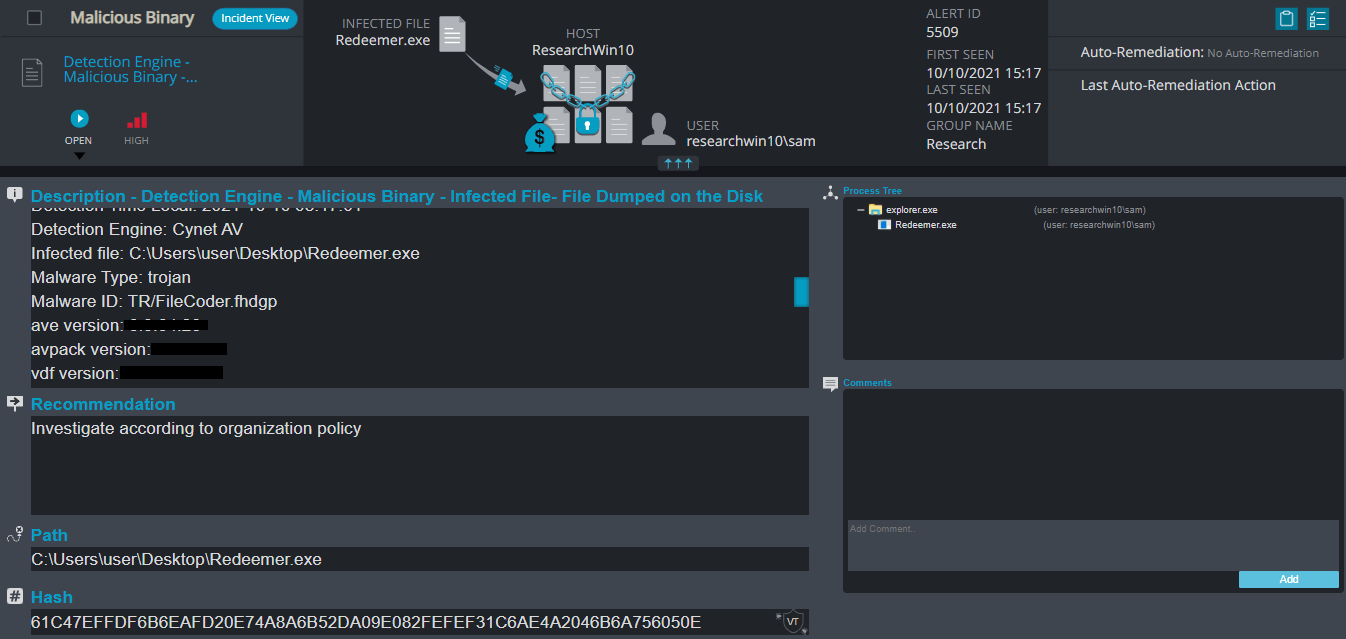
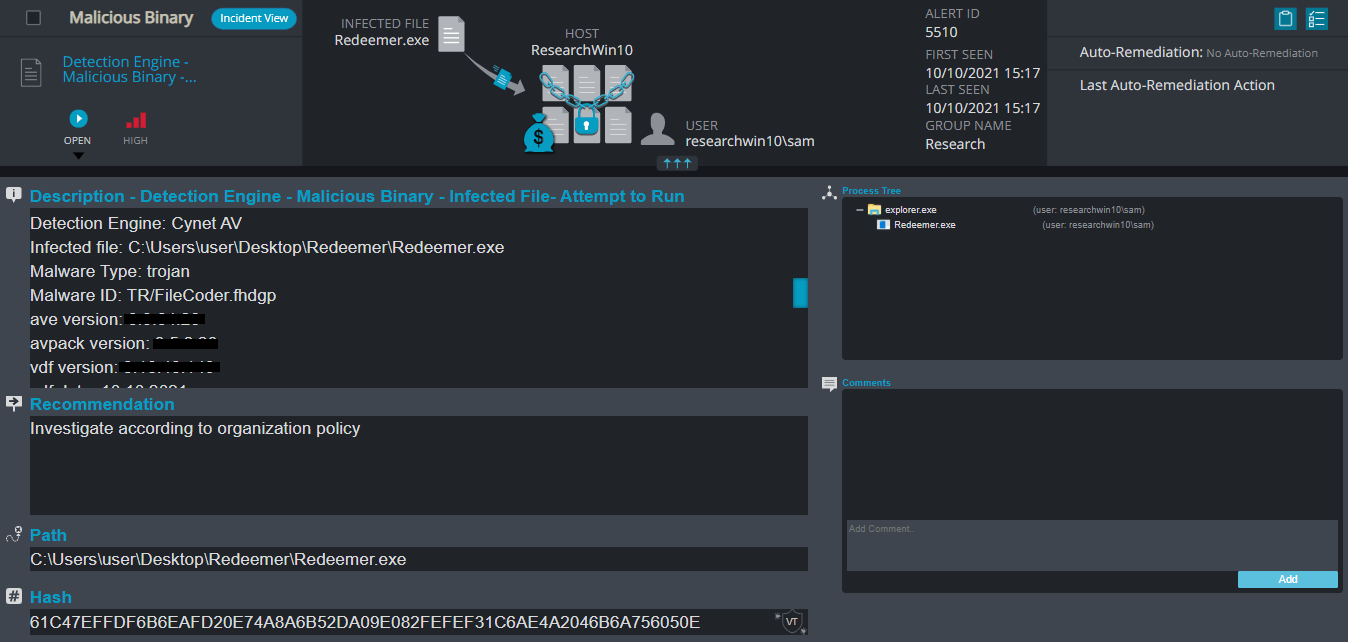
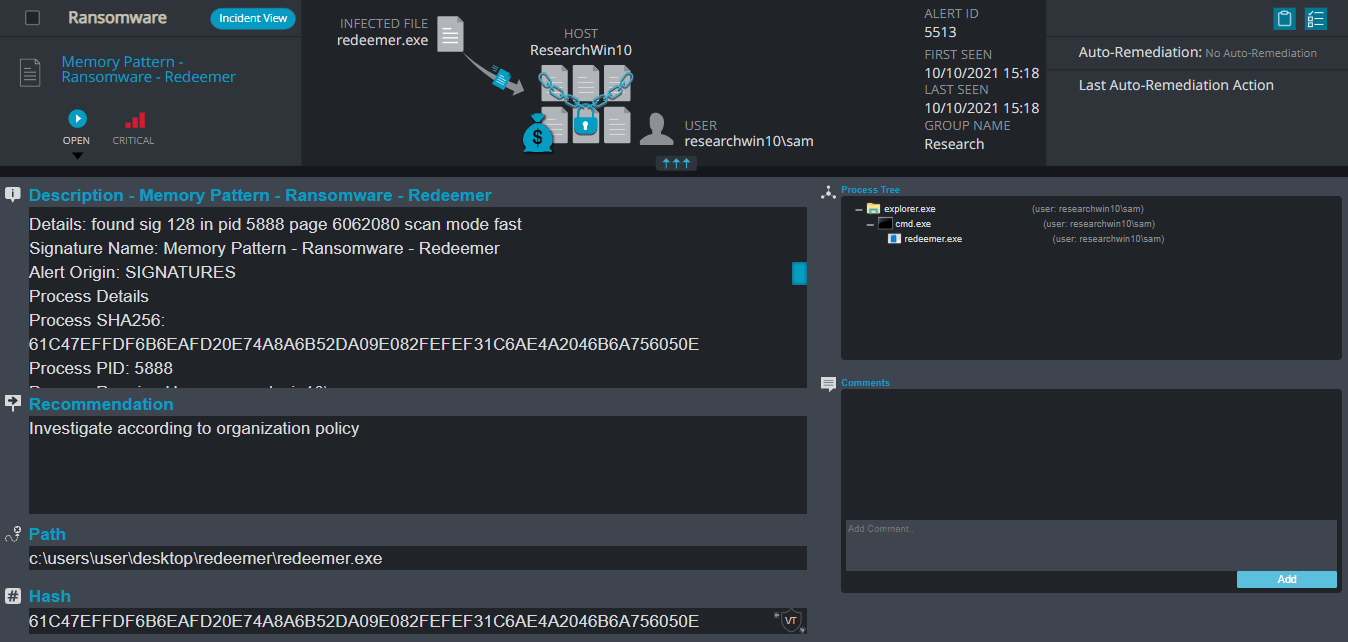
Cynet 360 Detections:
Redeemer Overview
Redeemer ransomware renames the encrypted files to .redeem in the extension for each file:
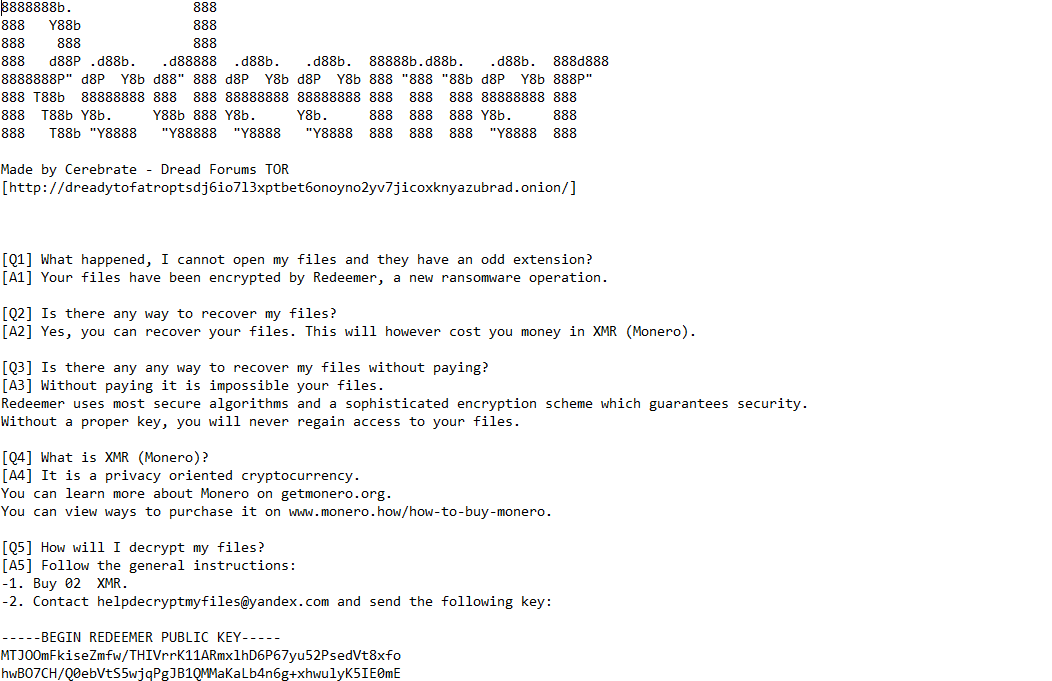
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file “Read Me.TXT” in the encrypted folders. The note contains the attacker’s Bitcoin address and the public encryption key. The note also includes a demand for ransom paid in Monero.
Yandex Ransomware
- Observed since: September 2021
- Ransomware extension: .yandex
- Ransomware note: READ_ME_NOW.txt
- Sample hash: 85e70eb088b0a36ab3947491789a024b1055c81984114834acd35c79958b5aa5
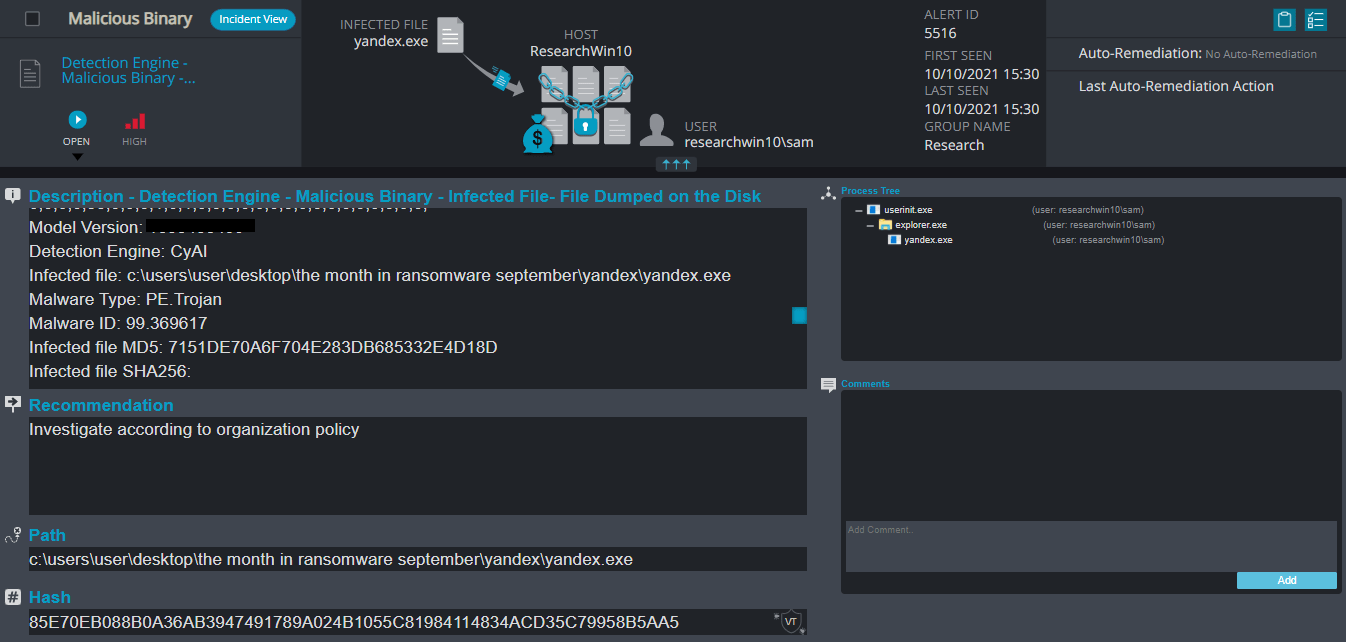
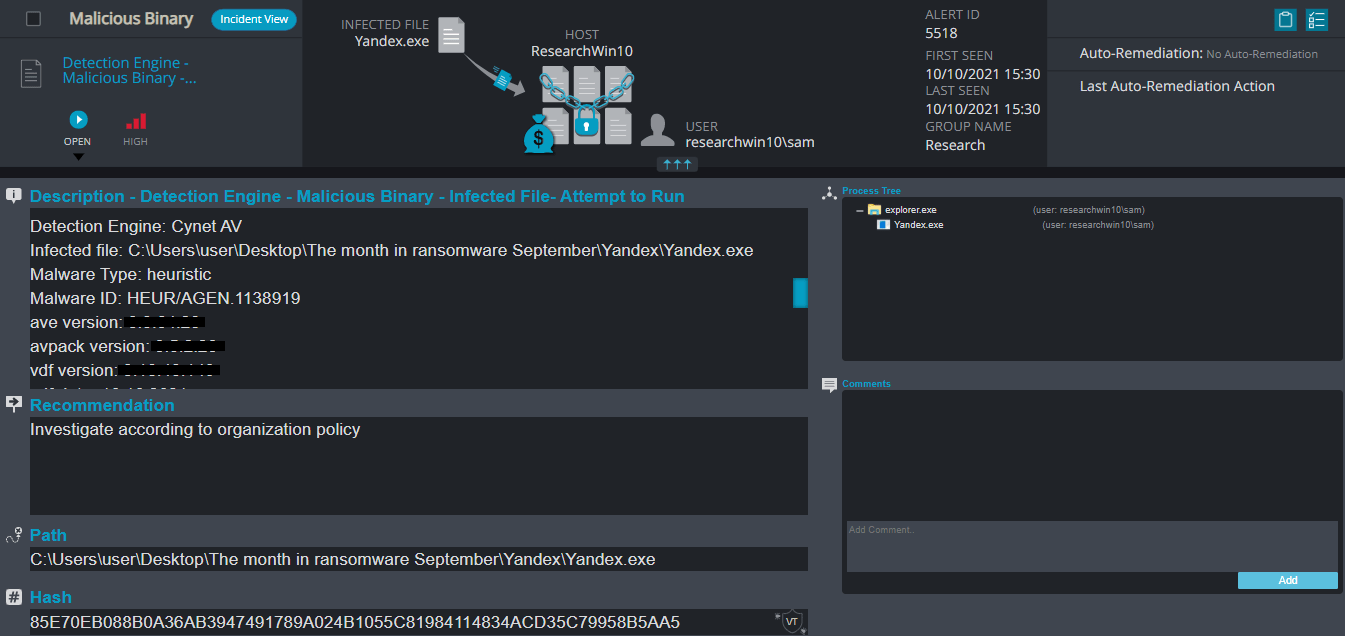
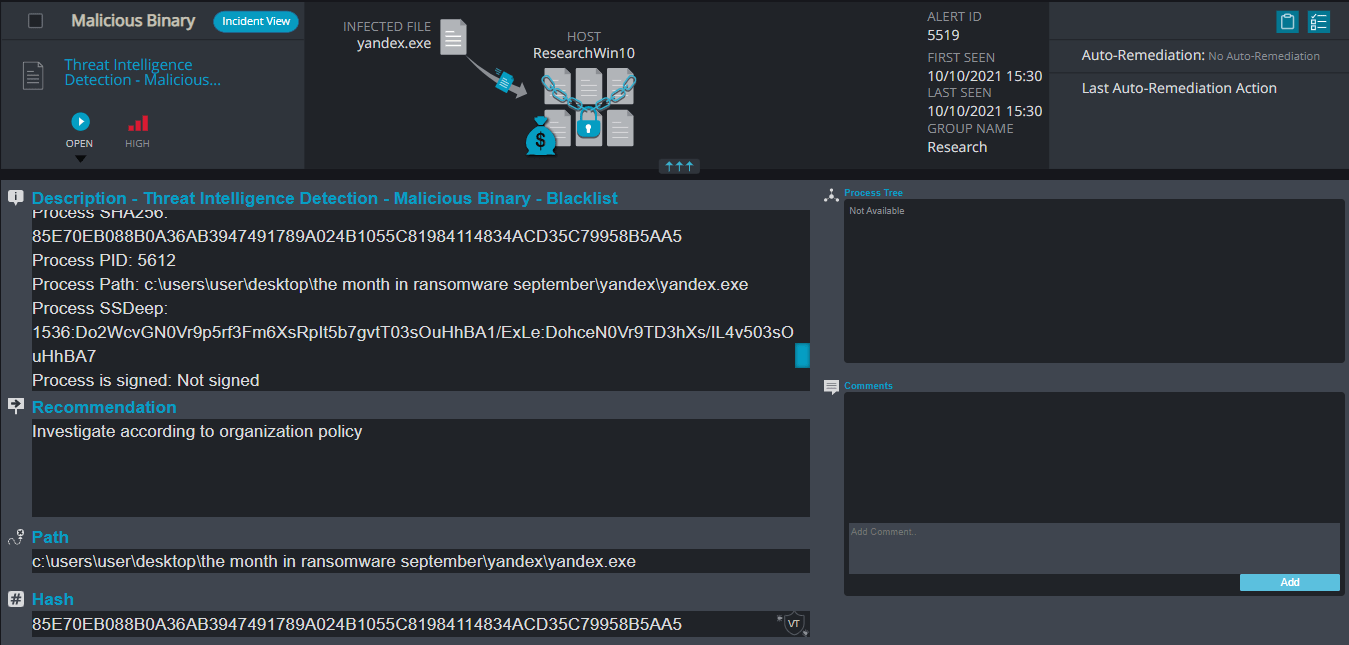
Cynet 360 Detections:
Yandex Overview
Yandex ransomware renames the encrypted files to .yandex in the extension for each file:
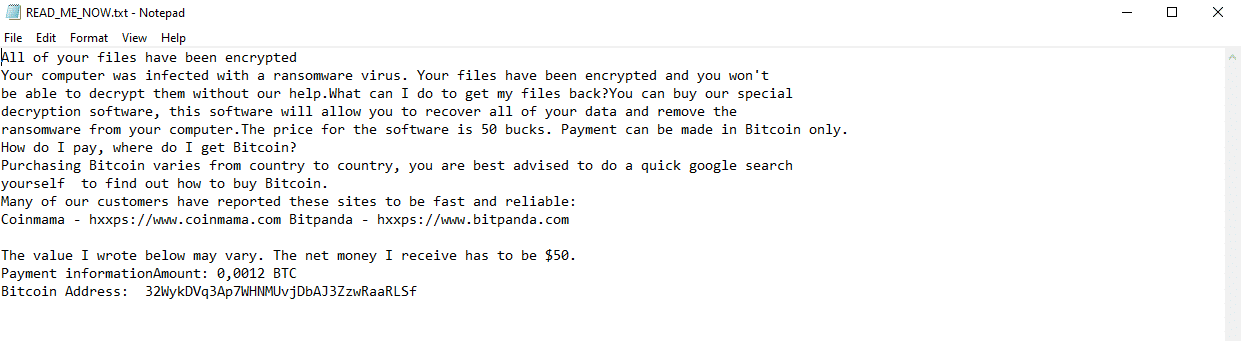
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops the ransomware note as a text file “READ_ME_NOW.txt” in the encrypted folders and changes the desktop background. The note contains the attacker’s Bitcoin address and the decryption price
CYNET VARIOUS MECHANISMS
- AV/AI – This alert triggers when Cynet’s AV/AI engine detects a malicious file that was either dumped on the disk or executed
- Malicious Binary – This alert triggers when Cynet detects a file that is flagged as malicious in Cynet’s EPS (endpoint scanner) built-in threat intelligence database. This database contains only critical IoCs (such as IOCs of ransomware, hacking tools, etc.).
- Memory Pattern – This alert triggers when Cynet detects memory strings that are associated with Malware or with malicious files
- Ransomware Heuristic – This alert triggers when Cynet detects suspicious behavior which can be associated with Ransomware (such as changing file extensions to “.Lock”).
- Malicious Binary – Process Create Malicious File – This alert triggers when Cynet detects a process that creates a file that is either flagged as malicious in Cynet’s Threat Intelligence database, or associated with suspicious patterns (such as loaded to sensitive directories).
- Process Monitoring – This alert triggers when a process runs with certain parameters which can indicate suspicious activity (for example, a vssadmin with suspicious parameters such as delete shadow copies).
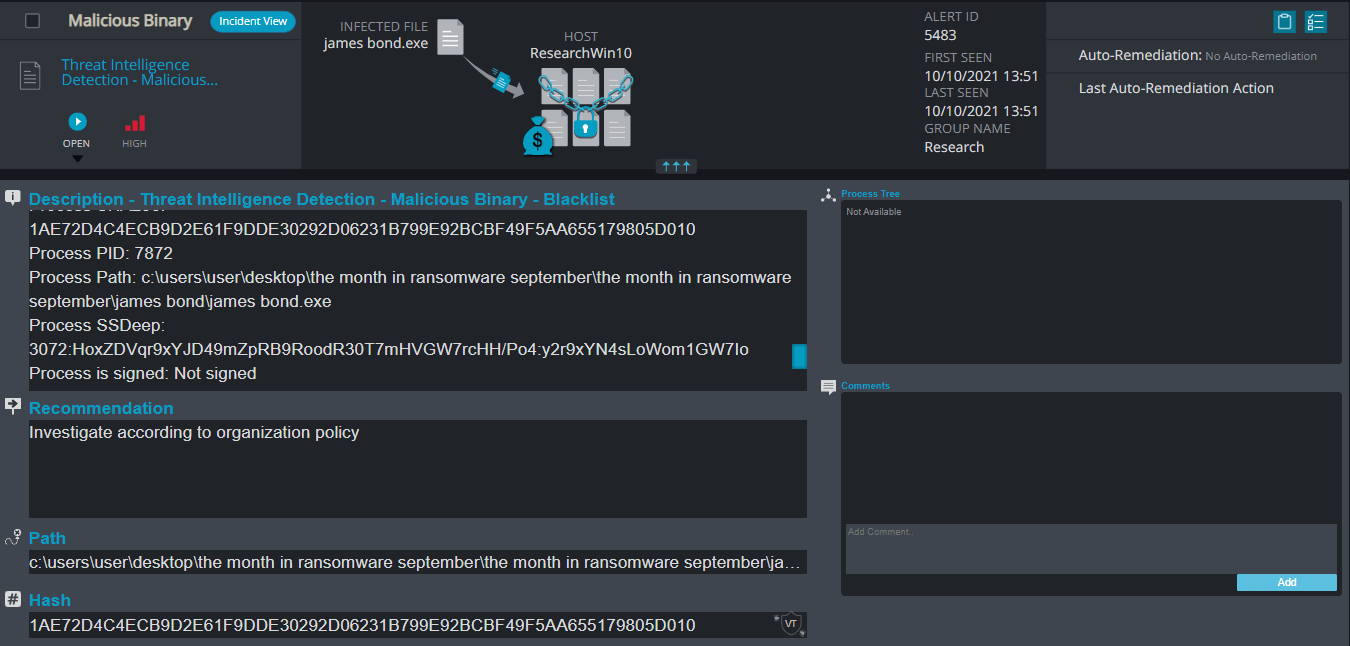
- Threat Intelligence Detection – Malicious Binary – This alert triggers when Cynet detects a file that is flagged as malicious in Cynet’s internal threat intelligence database.