June 2022 Ransomware Activity Report
Written by: Maor Huli
In the month of June, the ransomware that was introduced:
- MoonShadow
- Phobos
- Linda
- Sheeva
- Ritzer
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Orion is an integral department in Cynet’s research team that works around the clock to track threat intelligence resources, analyze payloads, and automate labs to ensure that our customers are protected against the newest ransomware variants. In these monthly reports, Orion reviews the latest trends identified in Bleeping Computer – the most up-to-date website that summarizes the newest ransomware variants – and shares how Cynet detects against these threats.
CYNET 360 AutoXDR™ VS RANSOMWARE
- Observed since: June 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .moonshadow
- Ransomware note: Decryption-Guide.txt | .hta
- Sample hash: ac2d92c801261e1887ad6a9dbbf52e08d9e3193976de096fb361597736a8c1ac
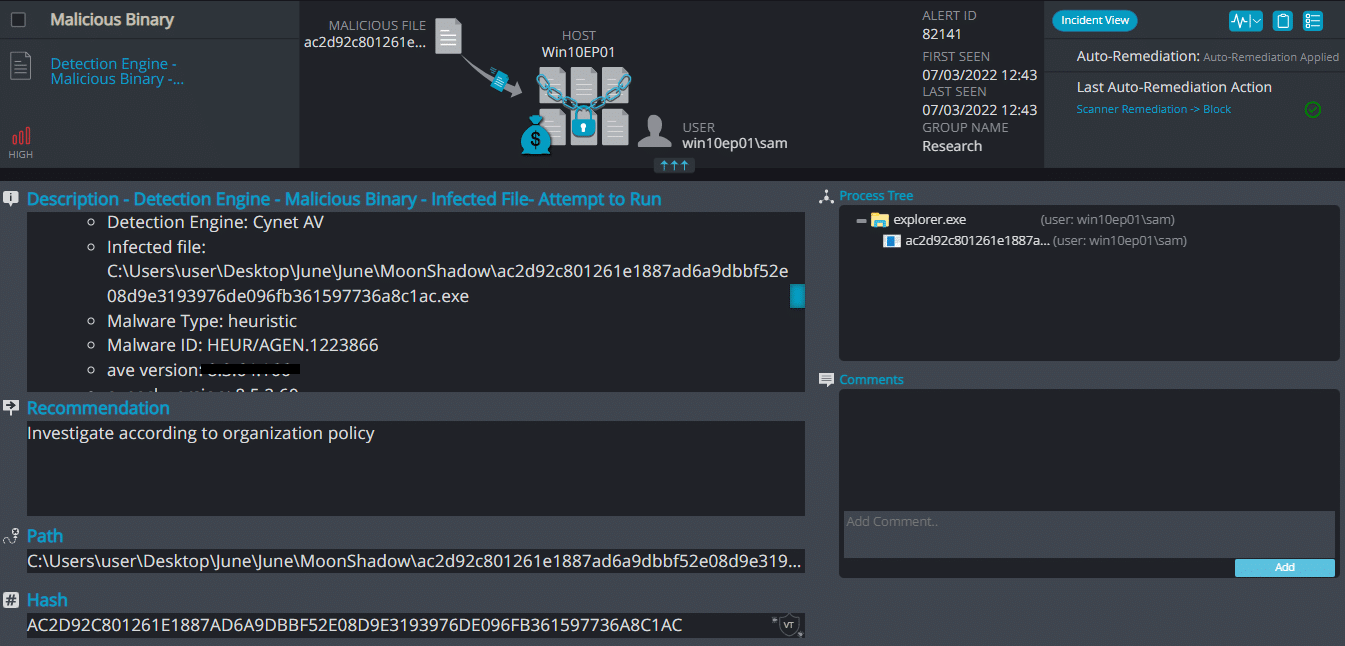
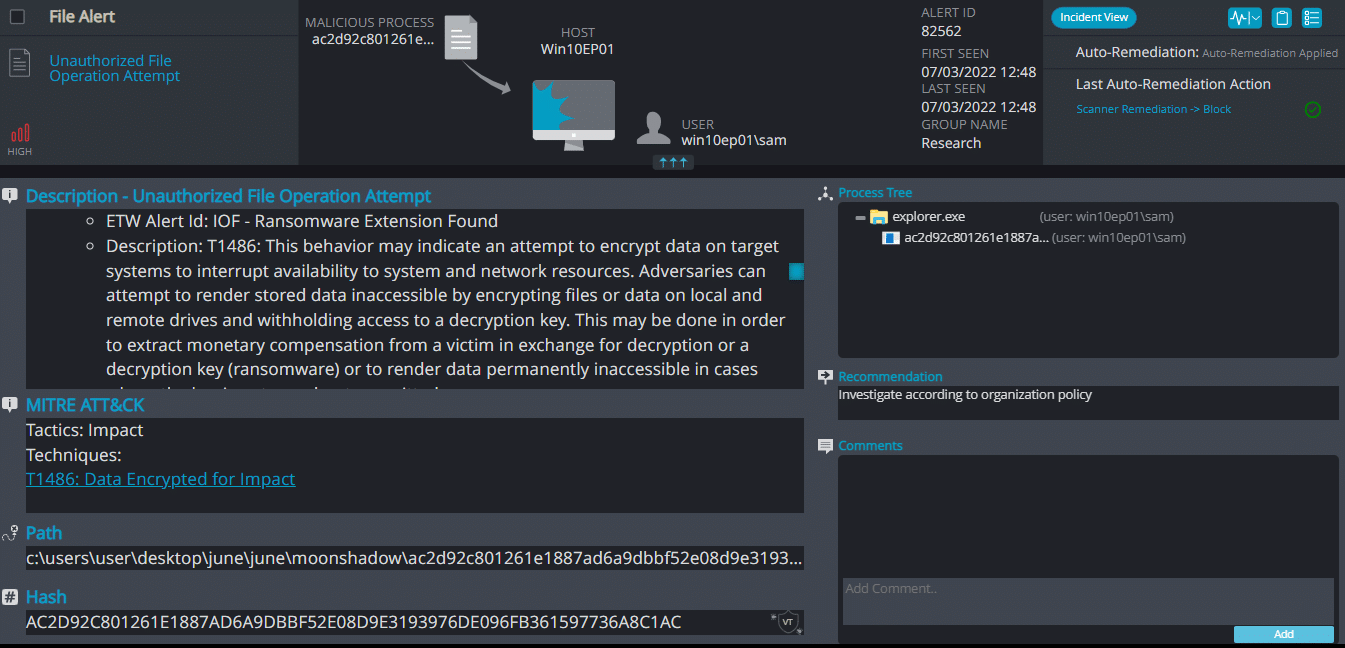
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
MoonShadow ransomware is supposed to rename the encrypted files with .moonshadow in the extension.
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as Decryption-Guide.HTA|.txt:
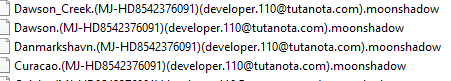
The ransomware note contains general information, warnings, and the attacker’s email address:
Phobos Ransomware
- Observed since: late 2017
- Ransomware encryption method: AES
- Ransomware extension: .decrypt
- Ransomware note: info.txt
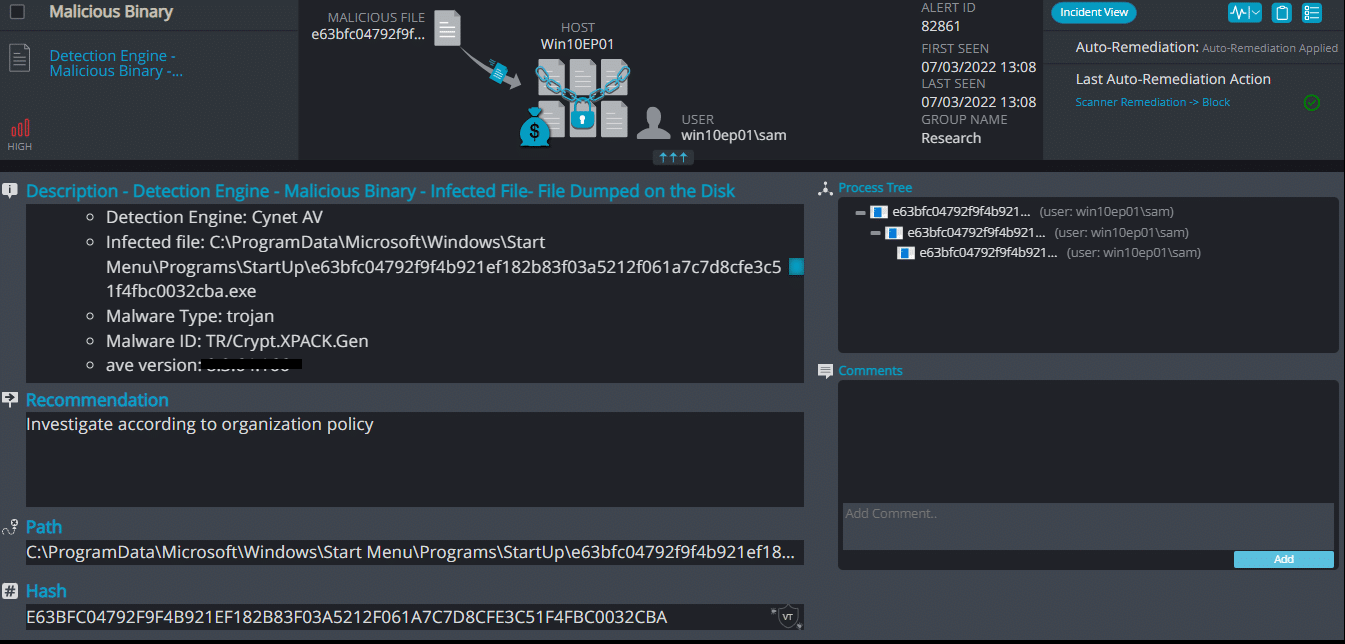
- Sample hash: e63bfc04792f9f4b921ef182b83f03a5212f061a7c7d8cfe3c51f4fbc0032cba
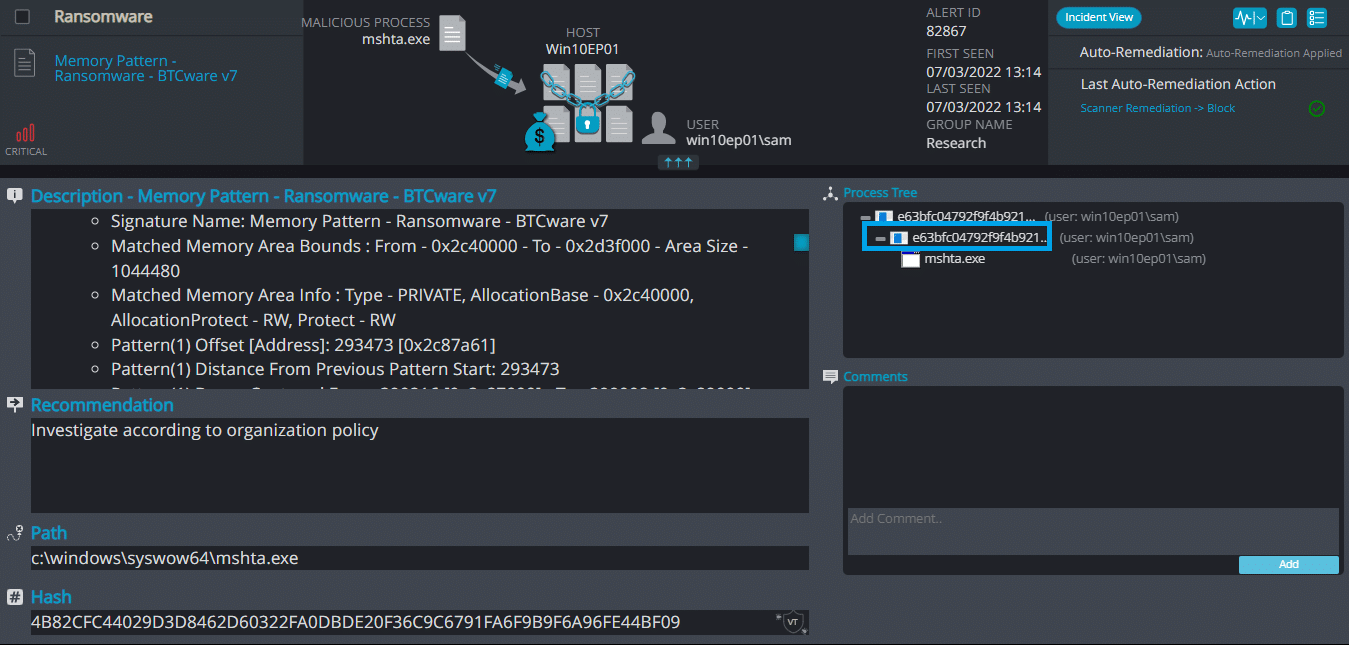
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
Phobos ransomware renames the encrypted files with .decrypt in the extension:
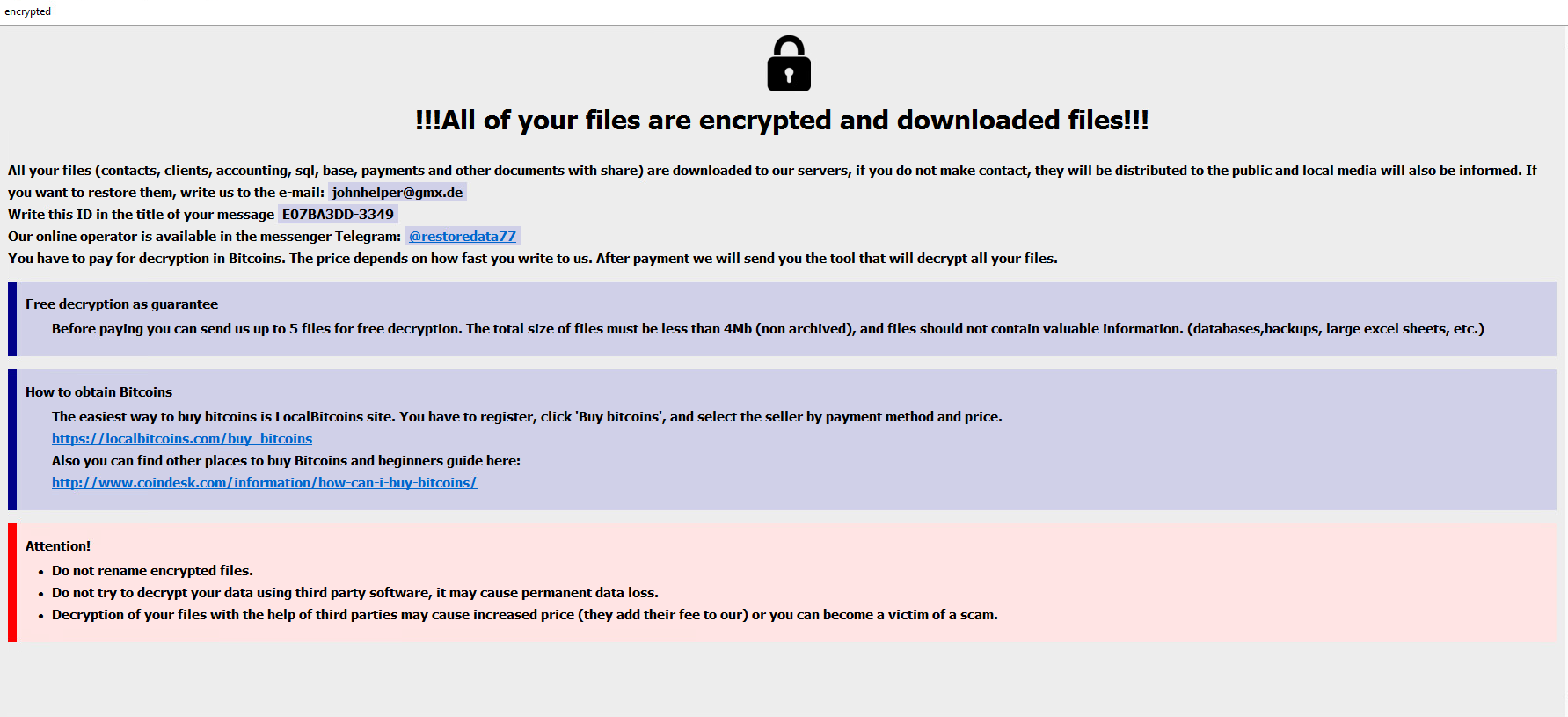
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it attempts to drop the ransomware note named info.txt:
The ransomware note contains general information, warnings, and the attacker’s telegram and email:
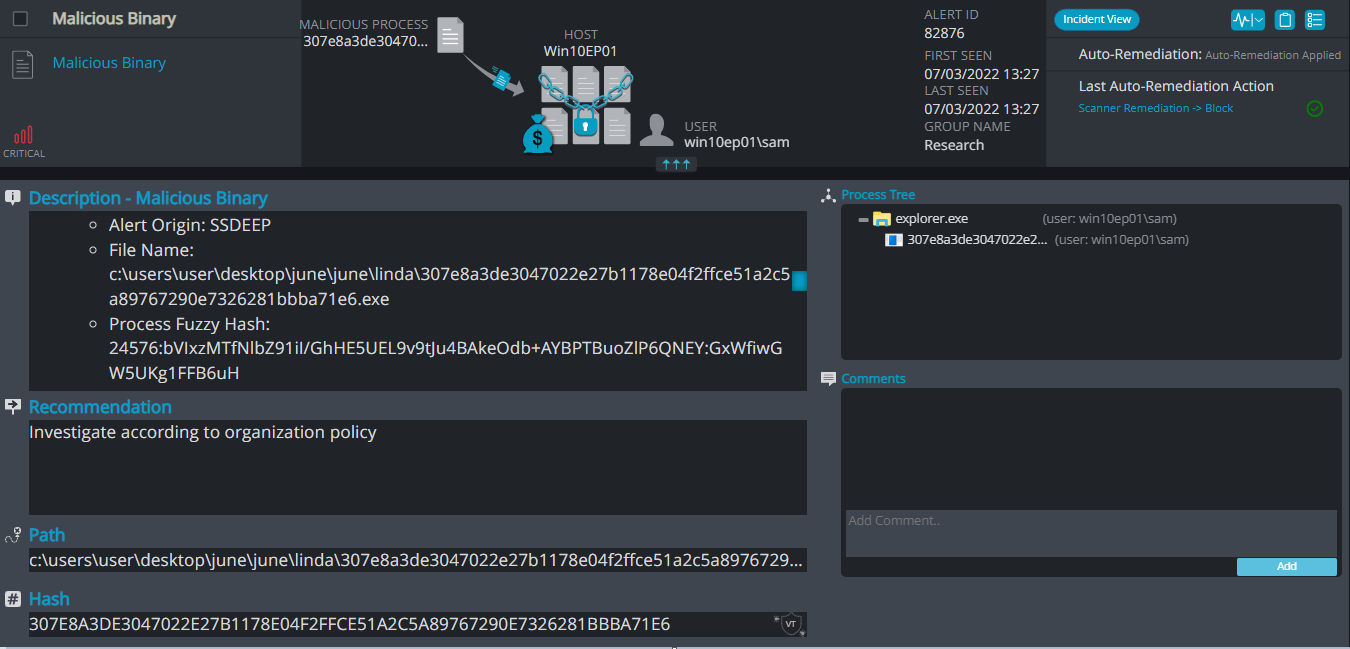
Linda Ransomware
- Observed since: June 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .linda
- Ransomware note: !info.hta
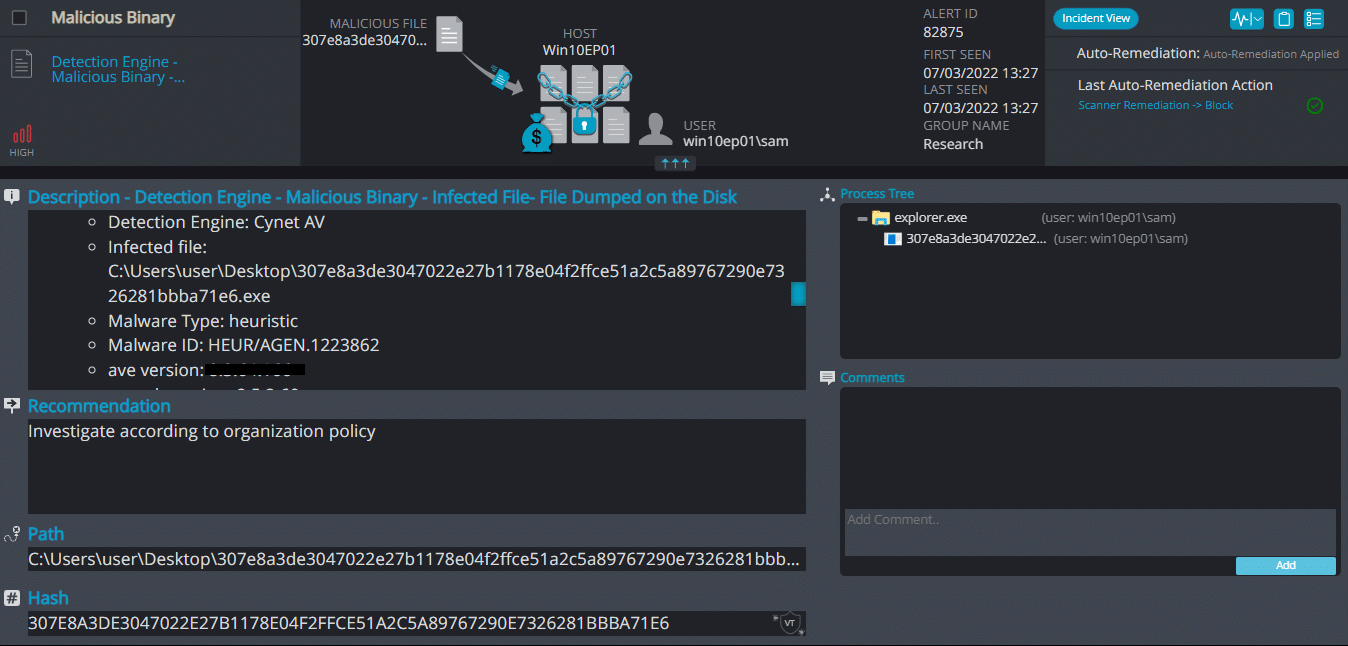
- Sample hash: 307e8a3de3047022e27b1178e04f2ffce51a2c5a89767290e7326281bbba71e6
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
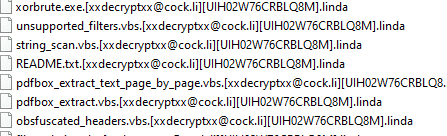
Linda ransomware renames the encrypted files with .linda in the extension:
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note named !INFO.HTA:
The ransom note contains general information, warnings, and the attacker’s email:
- Observed since: June 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .sheeva
- Ransomware note: sheeva.txt
- Sample hash: 991d018090cfd0b39d562010abf24b169ed55bea2d1bfc3044622e2ade3827d7
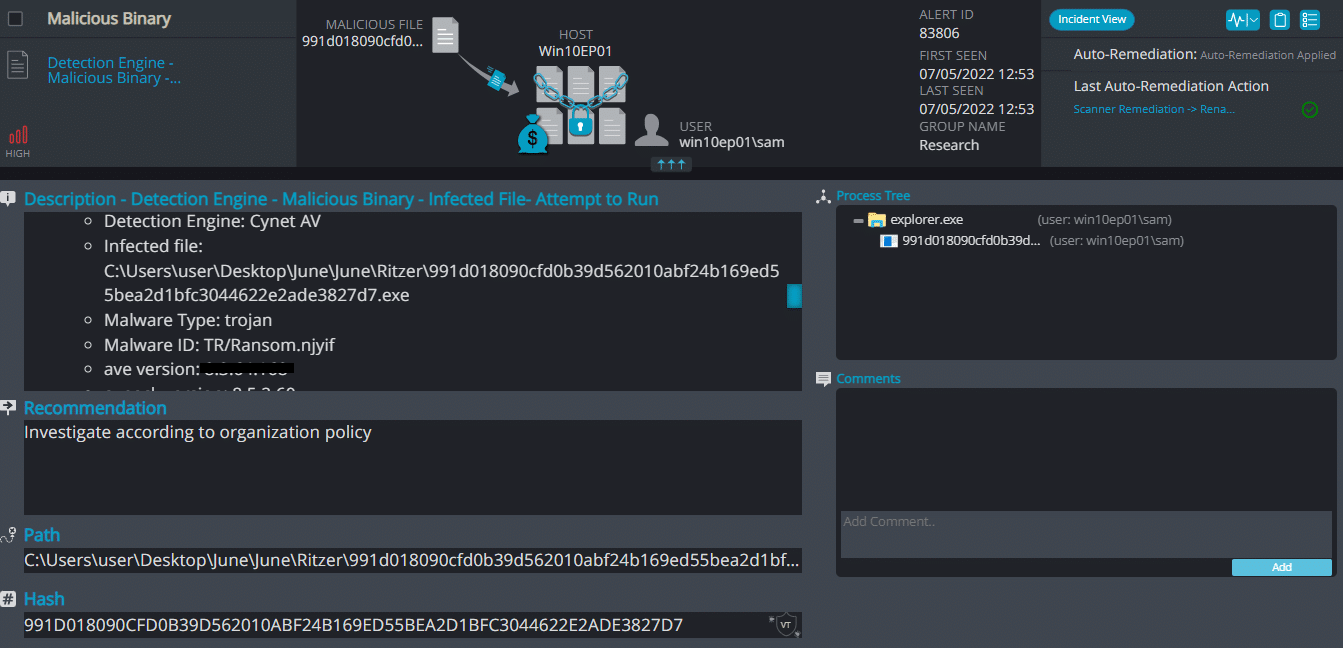
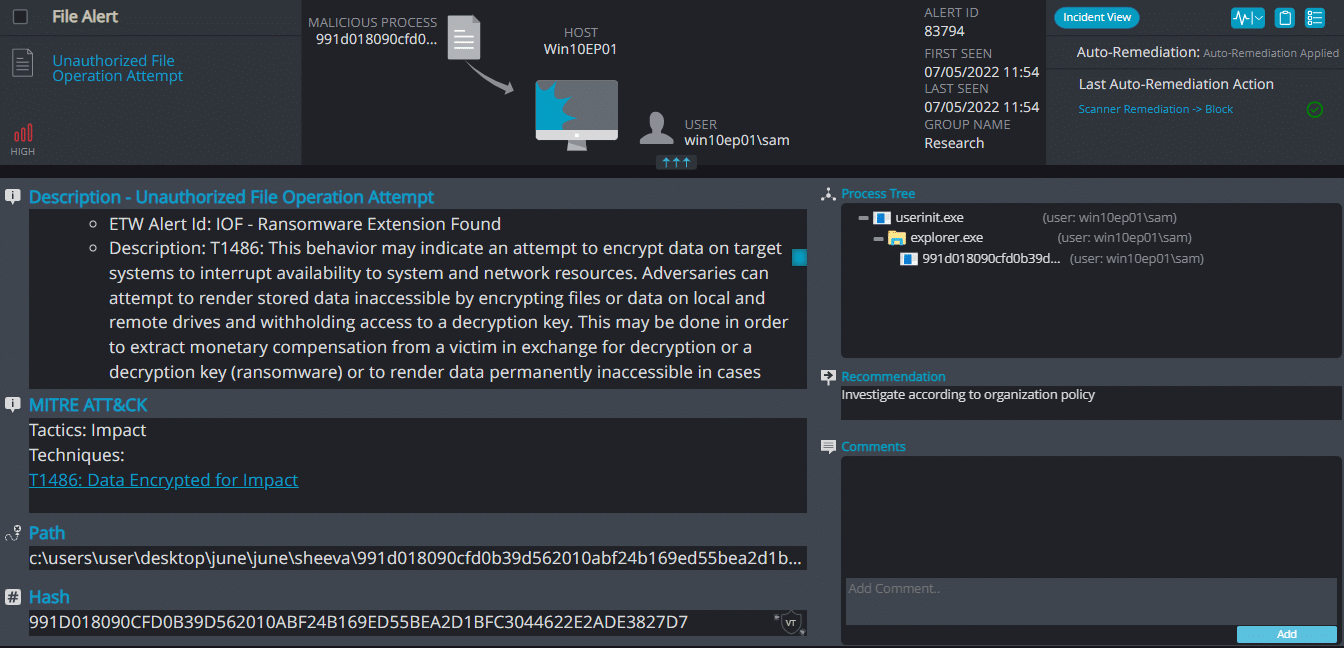
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
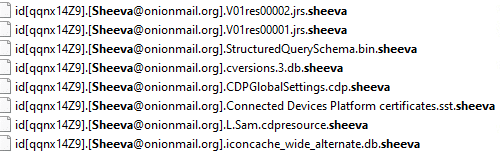
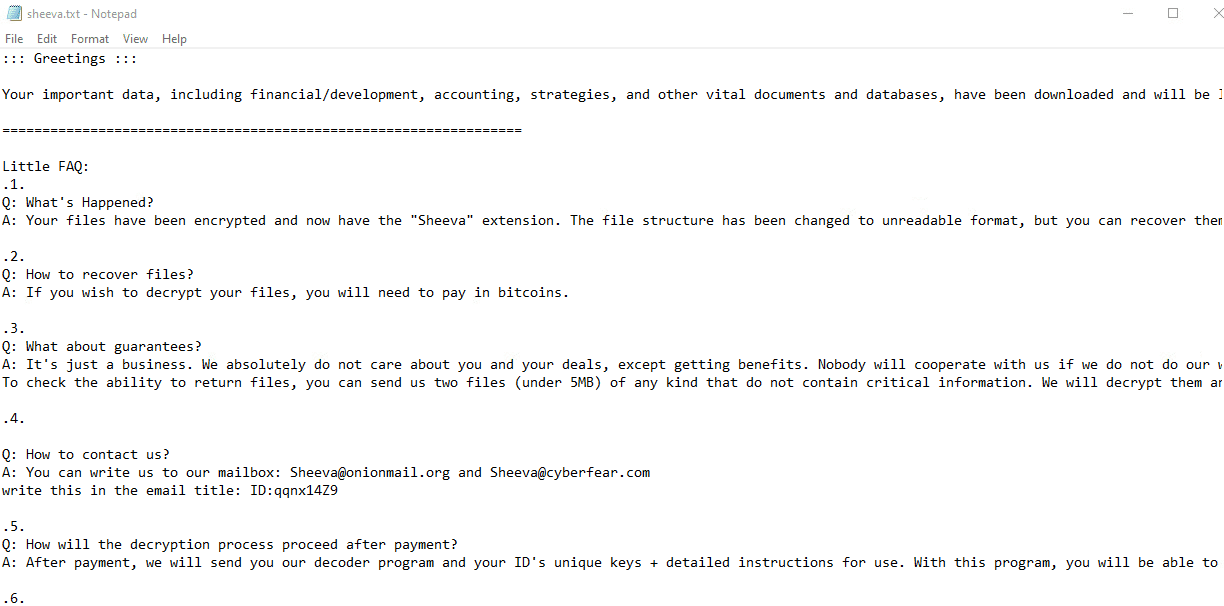
Sheeva ransomware renames the encrypted files with .sheeva in the extension:
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as sheeva.txt:
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions and the attacker’s contact info:
Ritzer Ransomware
- Observed since: June 2022
- Ransomware encryption method: AES + RSA
- Ransomware extension: .ritzer
- Ransomware note: read_it.txt
- Sample hash: fe5b33909638954acc556be872ee86f0e2a926f96ead41392923d31e9221ff10
Cynet 360 AutoXDR™ Detections:
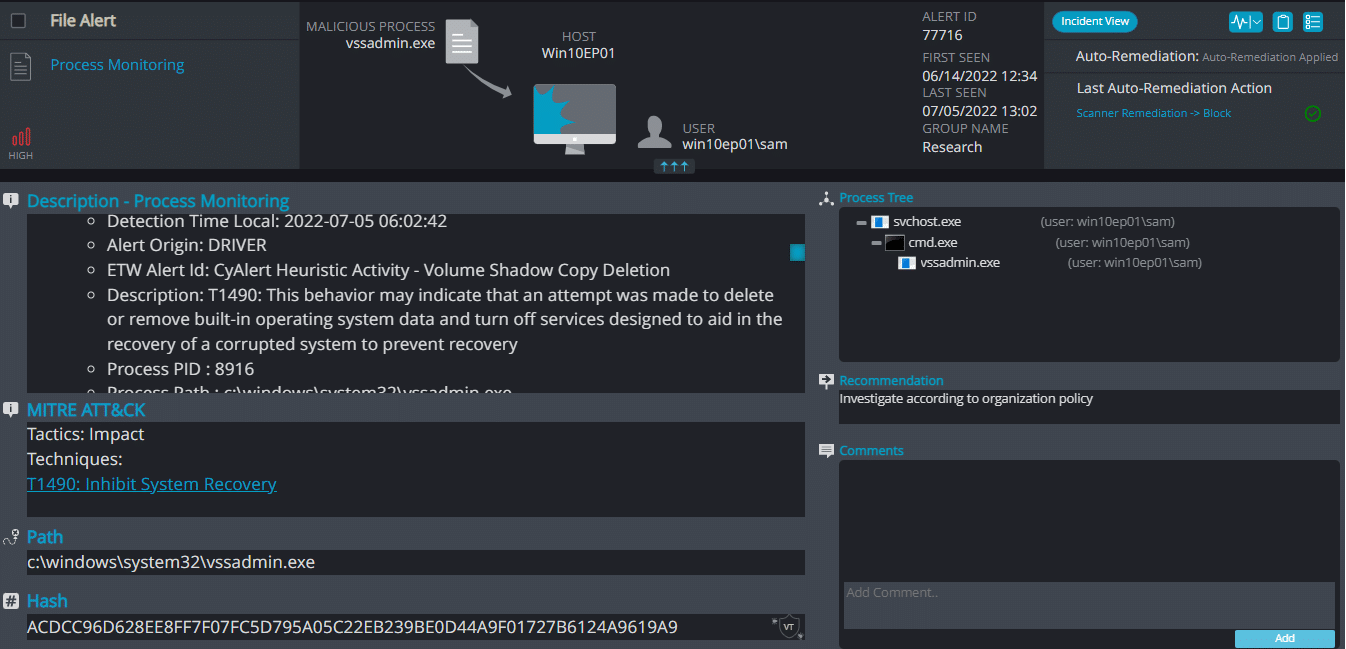
Ritzer Overview
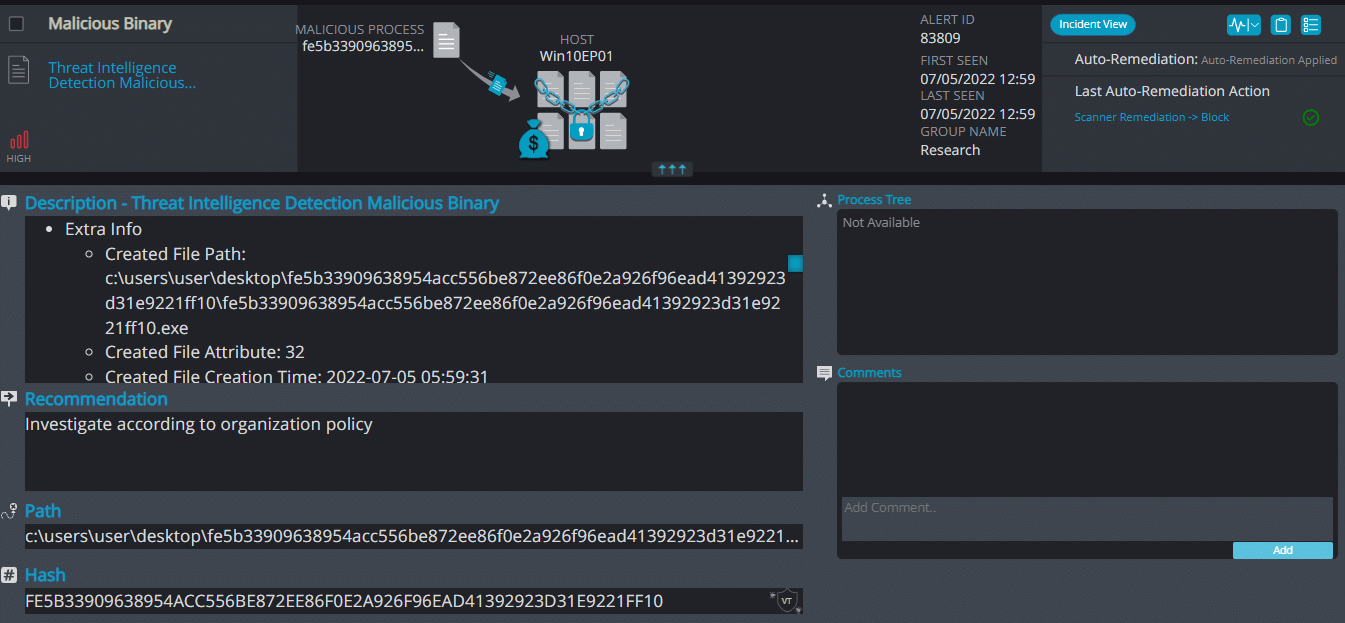
Ritzer ransomware renames the encrypted files with .ritzer in the extension:
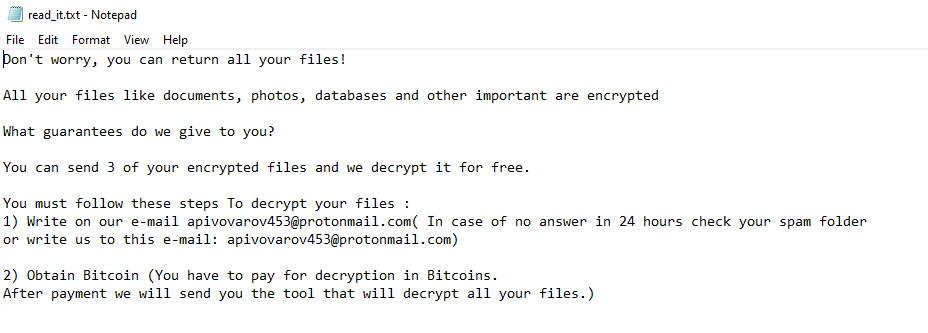
Once a computer’s files have been encrypted and renamed, it drops a note as read_it.txt:
Upon execution, it immediately encrypts the endpoint and drops the ransomware note. The ransomware note contains instructions and the attacker’s contact information: